RGD peptide-functionalized micelles loaded with crocetin ameliorate doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity
- PMID: 40103672
- PMCID: PMC11914822
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpx.2025.100326
RGD peptide-functionalized micelles loaded with crocetin ameliorate doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity
Abstract
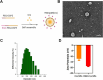
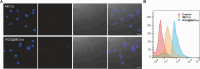
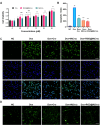
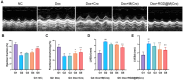
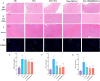
Doxorubicin (Dox)-induced cardiotoxicity presents a significant challenge to fully harnessing its chemotherapeutic potential. Crocetin (Cro), a dicarboxylic acid found in the crocus flower and gardenia fruit, has shown remarkable antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. However, its poor aqueous solubility and limited cellular uptake severely constrain its further application in treating diseases. In this study, we developed Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) peptide-decorated nanomicelles delivering Cro to alleviate Dox-induced cardiac injury. The RGD@M(Cro) nanomicelles exhibited excellent aqueous solubility and a drug-loading efficiency of 93.3 %. RGD-decorated micelles could enhance the cellular uptake of Cro in cardiomyocytes and inhibit approximately 60 % of HL-1 cell apoptosis through efficient reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging. In a cardiomyopathy mouse model, RGD@M(Cro) substantially reduced cardiac damage and improved cardiac indicators. This study highlights the great potential of RGD-decorated micelles in treating cardiac injury and other diseases.
Keywords: Antioxidant effect; Cardiotoxicity; Crocetin; Drug delivery; RGD peptide.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Alipour M., Baneshi M., Hosseinkhani S., Mahmoudi R., Jabari Arabzadeh A., Akrami M., Mehrzad J., Bardania H. Recent progress in biomedical applications of RGD-based ligand: from precise cancer theranostics to biomaterial engineering: a systematic review. J. Biomed. Mater. Res.t A. 2020;108:839–850. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.36862. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

