Research progress on the use of the optical coherence tomography system for the diagnosis and treatment of central nervous system tumors
- PMID: 40103695
- PMCID: PMC11911102
- DOI: 10.1002/ibra.12184
Research progress on the use of the optical coherence tomography system for the diagnosis and treatment of central nervous system tumors
Abstract
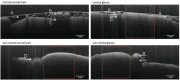
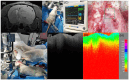
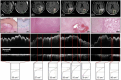
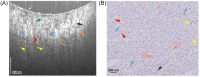
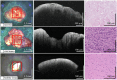
In central nervous system (CNS) surgery, the accurate identification of tumor boundaries, achieving complete resection of the tumor, and safeguarding healthy brain tissue remain paramount challenges. Despite the expertise of neurosurgeons, the infiltrative nature of the tumors into the surrounding brain tissue often hampers intraoperative differentiation between tumorous and non-tumorous tissue, thus hindering total tumor removal. Optical coherence tomography (OCT), with its unique advantages of high-resolution imaging, efficient image acquisition, real-time intraoperative detection, and radiation-free and noninvasive properties, offers accurate diagnostic capabilities and invaluable intraoperative guidance for minimally invasive CNS tumor diagnosis and treatment. Various OCT systems have been employed in neurological tumor research, including polarization-sensitive OCT systems, orthogonal polarization OCT systems, Doppler OCT systems, and OCT angiography systems. In addition, OCT-based diagnostic and therapeutic techniques have been explored for the surgical resection of CNS tumors. This review aims to compile and evaluate the research progress surrounding the principles of OCT systems and their applications in CNS tumors, providing insights into potential future research avenues and clinical applications.
Keywords: animal models; intraoperative real‐time detection; optical coherence tomography system; tumor boundary detection.
© 2024 The Author(s). Ibrain published by Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University (AHZMU) and Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
Jing Li, who is affiliated with Chengdu Incrpeak Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd., Optoelectric Industrial Park, Chengdu 610207, China, declares as only being the co‐author, and no such hidden identity/information/consequence which will become the influence of this study. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Optical coherence tomography for precision brain imaging, neurosurgical guidance and minimally invasive theranostics.Biosci Trends. 2018 Mar 18;12(1):12-23. doi: 10.5582/bst.2017.01258. Epub 2018 Jan 15. Biosci Trends. 2018. PMID: 29332928 Review.
-
Imaging of human brain tumor tissue by near-infrared laser coherence tomography.Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2009 May;151(5):507-17; discussion 517. doi: 10.1007/s00701-009-0248-y. Epub 2009 Apr 3. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2009. PMID: 19343270 Free PMC article.
-
OCT-Guided Surgery for Gliomas: Current Concept and Future Perspectives.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Jan 28;12(2):335. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12020335. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35204427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Time-domain and spectral-domain optical coherence tomography in the analysis of brain tumor tissue.Lasers Surg Med. 2006 Jul;38(6):588-97. doi: 10.1002/lsm.20353. Lasers Surg Med. 2006. PMID: 16736504
-
Cross-Polarization Optical Coherence Tomography for Brain Tumor Imaging.Front Oncol. 2019 Apr 2;9:201. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00201. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31001471 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
