Use of multiple indicators multiple causes (MIMIC) method to investigate quantitative inference in socioeconomic determinants on motorcyclist stress
- PMID: 40103770
- PMCID: PMC11919320
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mex.2025.103240
Use of multiple indicators multiple causes (MIMIC) method to investigate quantitative inference in socioeconomic determinants on motorcyclist stress
Abstract
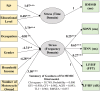
Research has shown that driving-related stress plays a significant role in causing traffic accidents, either directly or indirectly. Motorcyclists often engage in risky driving behaviors due to elevated stress levels. This study investigates the influence of socioeconomic factors on driving stress among motorcyclists. Data were gathered from 50 participants, with heart rate (HR) recorded using the Polar Vantage V2 device. Heart rate variability (HRV) was analyzed in both time and frequency domains using Kubios HRV software. The study employed the Multiple Indicators Multiple Causes (MIMIC) model to explore the associations between socioeconomic factors and driving stress. The results indicate that variables such as age, gender, education level, occupation, income, driving experience, and travel purpose significantly affect stress levels across both HRV domains. These findings highlight the importance of addressing motorcyclist stress through targeted interventions, including educational programs and policy measures that regulate driving duration. Such strategies are particularly vital in developing countries to reduce stress and improve road safety. This research provides a foundation for developing practical solutions aimed at minimizing driving stress and enhancing the well-being of motorcyclists in high-risk environments.•A MIMIC model was applied to analyze the relationship between stress variables in the time and frequency domains based on HRV data.•The model identified significant causal relationships, emphasizing the pivotal role of socioeconomic factors in influencing motorcyclists' driving stress.•The model demonstrated strong statistical performance with key indicators: chi-square = 38.749, GFI = 0.958, CFI = 0.982, AGFI = 0.893, TLI = 0.961, and RMSEA = 0.057, confirming its robustness and reliability.
Keywords: Driver stress; Heart rate variability; MIMIC; Multiple Indicators Multiple Causes (MIMIC); Safe driving; Socio-economic.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Magaña V.C., Pañeda X.G., Garcia R., Paiva S., Pozueco L. Beside and behind the wheel: factors that influence driving stress and driving behavior. Sustainability. 2021;13(9) doi: 10.3390/su13094775. - DOI
-
- Thwe P.P., Yamamoto T., Sato H., Morikawa T. Effect of roadway conditions and land-use on driving stress in Yangon, Myanmar. Asian Transp. Stud. 2018;5(2):408–422.
-
- Thwe P.P., Yamamoto T., Sato H., Morikawa T. Analysis of driving stress on various roadway conditions in Myanmar by using heart rate variability. Asian Transp. Stud. 2017;4(4):663–679.
-
- Meilinda I.M., Sugiarto S., Saleh S.M., Achmad A., Abubakar A. AIP Conference Proceedings. AIP Publishing; 2024. Preliminary analysis on heart rate (HR) and respiration rate (RR) of motorcyclists on urban arterial road.
-
- Meilinda I.M., Sugiarto S., Saleh S.M., Achmad A., Abubakar A. E3S Web of Conferences. EDP Sciences; 2024. Driving stress partial model considering time domain applying for two wheelers drivers: a case of primary arterial roads; p. 01043.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous