HEPNET Position Statement-I, Case Definition, Classification, Screening & Diagnosis of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) in Pakistan: A Resource for Primary and Secondary Care Physicians
- PMID: 40103882
- PMCID: PMC11911726
- DOI: 10.12669/pjms.41.3.10081
HEPNET Position Statement-I, Case Definition, Classification, Screening & Diagnosis of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) in Pakistan: A Resource for Primary and Secondary Care Physicians
Abstract
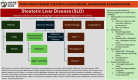
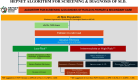
The Hep-Net position paper comes at a significant time in the history of Metabolically Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD) due to the rapid rise in this disease entity in the past decade. Metabolically Associated Fatty Liver Disease, by its very name, encompasses several common metabolic disease entities, top among those being diabetes and obesity. For Pakistan, the situation is serious as it is among the top 10 countries globally regarding the prevalence of obesity and number one in terms of diabetes, with over a quarter of adults affected. There remains slight ambiguity as regards the nomenclature of MAFLD, with western societies preferring to remove the word "fatty" and substitute with `'steatotic" i.e. MASLD. Regardless of names/titles the metabolic nature of the disease and its management remains the same and fortunately, that is something where universal consensus is present. Under the umbrella of Hep-Net, eminent hepatologists from all over Pakistan have pooled their efforts to formulate guidelines that are specifically tailored to the Pakistani population, its specific lifestyle and relevant interventions that are needed to treat fatty/steatotic liver disease. By virtue of its multi-systemic consequences, metabolic fatty liver disease represents the most significant and expensive disease entity, globally. Prevention, through public education and timely intervention in diagnosed cases will serve to avert a healthcare storm that will far outweigh viral hepatitis.
Keywords: Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease; metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease.
Copyright: © Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences.
Figures
Similar articles
-
From metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease to metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: Controversy and consensus.World J Hepatol. 2023 Dec 27;15(12):1253-1257. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v15.i12.1253. World J Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 38223415 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of nomenclature as metabolic associated steatotic liver disease on steatotic liver disease prevalence and screening: a prospective population survey in Asians.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Aug;39(8):1636-1647. doi: 10.1111/jgh.16554. Epub 2024 May 2. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38695344
-
Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Review and Position Statement of the Fatty Liver Research Group of the Korean Diabetes Association.Diabetes Metab J. 2024 Nov;48(6):1015-1028. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2024.0541. Epub 2024 Nov 21. Diabetes Metab J. 2024. PMID: 39610131 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Management of Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease/Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: From Medication Therapy to Nutritional Interventions.Nutrients. 2024 Jul 11;16(14):2220. doi: 10.3390/nu16142220. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39064665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-invasive Scores and Serum Biomarkers for Fatty Liver in the Era of Metabolic Dysfunction-associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD): A Comprehensive Review From NAFLD to MAFLD and MASLD.Curr Obes Rep. 2024 Sep;13(3):510-531. doi: 10.1007/s13679-024-00574-z. Epub 2024 May 29. Curr Obes Rep. 2024. PMID: 38809396 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ali Z, Riaz M, Alam A, Faroqi JI. Pakistan Society of Hepatology (PSH) Position Statement:Renaming Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) to Steatotic Liver Disease (SLD), Endorsement of New Multi-Society Nomenclature. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2023;35(4):700–702. doi:10.55519/JAMC-04-12433. - PubMed
-
- Eslam M, Sanyal AJ, George J, International Consensus P. MAFLD:A Consensus-Driven Proposed Nomenclature for Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology. 2020;158(7):1999–2014 e1. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2019.11.312. - PubMed
-
- Rinella ME, Lazarus JV, Ratziu V, Francque SM, Sanyal AJ, Kanwal F, et al. A multisociety Delphi consensus statement on new fatty liver disease nomenclature. J Hepatol. 2023;79(6):1542–1556. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2023.06.003. - PubMed
-
- Miao L, Targher G, Byrne CD, Cao YY, Zheng MH. Current status and future trends of the global burden of MASLD. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2024;35(8):697–707. doi:10.1016/j.tem.2024.02.007. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous