Associations of varicose veins with cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease pathologies in adults without dementia: the CABLE study
- PMID: 40103929
- PMCID: PMC11913850
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2025.1502154
Associations of varicose veins with cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease pathologies in adults without dementia: the CABLE study
Abstract
Background: Previous studies have found a correlation between varicose veins (VVs) and cognitive decline, and individuals with VVs have a higher prevalence of Alzheimer's disease (AD). However, the associations between VVs and the core pathologies of AD have not yet been investigated. The research was designed to analyze the relationships between VVs and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarkers of AD pathologies.
Methods: We included 1,298 participants from the Chinese Alzheimer's Biomarker and LifestylE (CABLE) database without dementia. Multiple linear regression (MLR) model was applied to assess the relationships between the VVs and CSF AD biomarkers. Then, we conducted subgroup analyses according to age, gender, education levels and apolipoprotein E genotype ε4 (APOE-ε4) carrier status. Additionally, mediation effects were assessed using causal mediation analyses with 10,000 bootstrapped iterations.
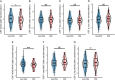
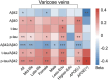
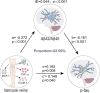
Results: In total subjects, VVs had negative correlations with CSF Aβ42 (β = -0.157, p = 0.038) and CSF Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio (β = -0.272, p < 0.001), as well as positive correlations with CSF Aβ40 (β = 0.170, p = 0.024), CSF p-tau (β = 0.192, p = 0.008), CSF t-tau/Aβ42 ratio (β = 0.190, p = 0.011), and CSF p-tau/Aβ42 ratio (β = 0.248, p = 0.001), after adjusting for age, sex, education levels and APOE-ε4 carrier status. Subgroup analyses demonstrated that the relations between VVs and CSF AD biomarkers were more significant in female, mid-life adults (40-65 years), less-educated individuals and APOE-ε4 non-carriers. Moreover, CSF Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio might be a partial mediator of the association between VVs and p-tau pathology.
Conclusion: Our study found correlations between VVs and CSF AD biomarkers, suggesting that VVs may be a potential risk factor for the development of AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; biomarkers; dementia; inflammation; varicose veins.
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Ma, Li, Huang, Hu, Tan and Hu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Associations between platelet indices and cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease pathology in cognitively intact adults: the CABLE study.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025 May 31;17(1):124. doi: 10.1186/s13195-025-01755-1. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40450373 Free PMC article.
-
Association of APOE ε4/ε4 with fluid biomarkers in patients from the PUMCH dementia cohort.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Mar 31;15:1119070. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1119070. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37065463 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein E genotype and the diagnostic accuracy of cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for Alzheimer disease.JAMA Psychiatry. 2014 Oct;71(10):1183-91. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2014.1060. JAMA Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 25162367
-
Association Between Carotid Plaque and Alzheimer's Disease Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers and Cognitive Function in Cognitively Intact Adults: The CABLE Study.J Alzheimers Dis. 2024;100(1):207-217. doi: 10.3233/JAD-240131. J Alzheimers Dis. 2024. PMID: 38848186
-
Correlation between Cerebrospinal Fluid Core Alzheimer's Disease Biomarkers and β-Amyloid PET in Chinese Dementia Population.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2022 May 18;13(10):1558-1565. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.2c00120. Epub 2022 Apr 27. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35476397
References
-
- Auzky O., Lanska V., Pitha J., Roztocil K. (2011). Association between symptoms of chronic venous disease in the lower extremities and cardiovascular risk factors in middle-aged women. Int. Angiol. 30 335–341. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

