Gene mutations linked to drug-resistant epilepsy in astrocytoma
- PMID: 40103938
- PMCID: PMC11913685
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1523468
Gene mutations linked to drug-resistant epilepsy in astrocytoma
Abstract
Introduction: Epilepsy is common in gliomas, particularly astrocytomas, even in patients who have undergone total tumor resection. Resistance to antiseizure drugs presents a significant challenge in managing epilepsy. Seizure outcomes after brain surgery for drug-resistant epilepsy (DRE) are heterogeneous and difficult to predict using models that evaluate current clinical, imaging, and electrophysiological variables. This study aimed to investigate possible correlations between genetic mutations and antiseizure resistance using whole-exome sequencing.
Methods: Tumor samples from a medical biobank were subjected to whole-exome sequencing, and the contribution of 64 genes from a previous report was analyzed.
Results: Fifteen patients had DRE. Compared to the patients who showed drug responsiveness, patients in the DRE group exhibited mutations in glutamate receptor genes (GRIA1, GRIK5, GRIN2B, or GRIN2C), ATRX, and the glutamate-S-transferase gene. No significant differences were found between the groups in terms of mutations in BRAF, Olig2, Ki-67, IDH, PIK3CA, p53, GRM, or BCL2A.
Discussion: These findings suggest that somatic gene mutations are closely linked to DRE. Identifying the molecular basis of antiseizure drug resistance is crucial for improving the management of DRE.
Keywords: astrocytoma; drug resistance; drug-resistant epilepsy; exome sequencing; receptors.
Copyright © 2025 Phabphal, Kaewborisutsakul, Leetanaporn, Choochuen, Tunthanathip, Navakanitworakul and Sangkhathat.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
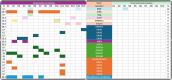
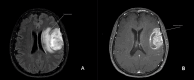
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

