Bibliometric and visualized analysis of research hotpots and future prospects in lacrimal duct obstruction disease (1900 to 2024)
- PMID: 40103946
- PMCID: PMC11865641
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2025.03.21
Bibliometric and visualized analysis of research hotpots and future prospects in lacrimal duct obstruction disease (1900 to 2024)
Abstract
Aim: To reveal the research hotspots, trends, and future prospects of lacrimal duct obstruction disease (LDOD) from 1900 to 2024 through the bibliometric and visualized analysis, providing a directional guidance for research in this field.
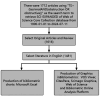
Methods: The Web of Science Core Collection database was used to retrieve relevant literature. Data analysis and visualization were conducted using VOSviewer 1.6.20 and CiteSpace 6.3.1, including annual publication volume, trends, research areas, country/region and institution distribution, journal and co-cited journal analysis, author and co-cited author analysis, keyword and burst keyword analysis, etc.
Results: The study included a total of 1481 articles, revealing an overall upward trend in research on LDOD, with ophthalmology being the predominant field. While the United States previously led research efforts, India and China have emerged as key contributors since 2015. Mohammad Javed Ali stands out as the most influential author in this research area. Ophthalmic Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery has published the highest number of related articles, whereas Ophthalmology has the highest co-citation. The current focal points of research include minimally invasive and precise modifications to dacryocystorhinostomy, along with intubation, new materials for stents, and disease pathogenesis.
Conclusion: LDOD research has garnered widely attention and exhibits a steady upward trend. Since 1900, the United States, China, and India have been the leading contributors to this field. Ophthalmologists continue to be the primary driving force behind LDOD research. The findings of this study suggest that at the forefront of LDOD research, our focus has long been on refining and innovating surgical treatment. The minimally invasive and precise modification of lacrimal surgery, represented by dacryocystorhinostomy, is the ongoing developmental direction of this field. Rapid interdisciplinary integration and in-depth exploration of pathogenesis and allergic inflammation will lead to the emergence of new materials, innovative technologies, and safer clinical treatment protocols.
Keywords: bibliometric analysis; dacryocystorhinostomy; lacrimal drainage system; lacrimal duct obstruction disease; tear drainage system.
International Journal of Ophthalmology Press.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: Chen MH, None; Bai F, None; Tao H, None.
Figures









References
-
- Raslan OA, Ozturk A, Pham N, et al. A comprehensive review of cross-sectional imaging of the nasolacrimal drainage apparatus: what radiologists need to know. Am J Roentgenol. 2019;213(6):1331–1340. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
