GPR120/FFAR4 protects retinal vascular endothelial cells against high glucose injury via suppressing ROS-ERS mediated apoptosis
- PMID: 40103966
- PMCID: PMC11865662
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2025.03.02
GPR120/FFAR4 protects retinal vascular endothelial cells against high glucose injury via suppressing ROS-ERS mediated apoptosis
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the role of reactive oxygen species-endoplasmic reticulum stress (ROS-ERS) in the cellular protection of G protein-coupled receptor 120 (GPR120/FFAR4) against high glucose (HG) induced human retinal vascular endothelial cell (HRVEC) injury and its underlying mechanisms.
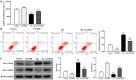
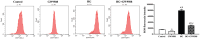
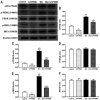
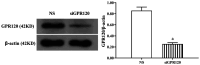
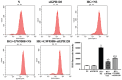
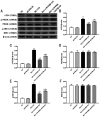
Methods: HRVECs were divided into the control group, GW9508 (an agonist of GPR120) group, HG group, and HG+GW9508 group. The cell proliferation and apoptosis were assessed by cell counting kit-8 and annexin V-FITC/PI apoptosis detection kit, respectively. Western blotting analysis was performed to assess the protein expressions of Bax, Bcl-2, activating transcription factor 6 (ATF6), PKR-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK), and inositol-requiring enzyme 1 (IRE1). The ROS assay kit was used for the detection of ROS production. Then the cells were transfected with siRNA of GPR120 and the ROS level and protein levels of ATF6, PERK, and IER1 were compared.
Results: GW9508 promoted the proliferation of HRVECs, which was significantly reduced by the stimulation of HG. GW9508 remarkably reduced the apoptosis rate of HRVECs under HG and the expression of proapoptotic protein Bax, while increased the expression of antiapoptotic protein Bcl-2. Under HG condition, a significant increase of ROS production was noticed in HRVECs, and GW9508 treatment greatly decreased it. The over-expressions of ERS-related proteins ATF6, PERK, and IER1 under HG were down-regulated by GW9508 treatment. After successfully transfected with siGPR120, the effects of GW9508 on the production of ROS as well as the expressions of ATF6, PERK, and IER1 were reversed.
Conclusion: GPR120 protects HRVECs against HG induced apoptosis, and suppressing ROS-ERS pathway is one of the mechanisms involved. Activation of GPR120 may be considered as a potential therapeutic target for diabetic retinopathy.
Keywords: GPR120/FFAR4; apoptosis; high glucose; oxidative stress; retinal vascular endothelial cells.
International Journal of Ophthalmology Press.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: Wang LZ, None; Yan JJ, None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Agonism of GPR120 Prevented High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis of Retinal Endothelial Cells through Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome.Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2023 Nov;240(11):1292-1299. doi: 10.1055/a-1811-7099. Epub 2022 May 18. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2023. PMID: 35584771 English.
-
GPR120 Agonist GW9508 Ameliorated Cellular Senescence Induced by ox-LDL.ACS Omega. 2020 Dec 8;5(50):32195-32202. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c03581. eCollection 2020 Dec 22. ACS Omega. 2020. PMID: 33376857 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK) signaling pathway plays a major role in reactive oxygen species (ROS)-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2013 Nov 2;12:158. doi: 10.1186/1475-2840-12-158. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2013. PMID: 24180212 Free PMC article.
-
Exenatide regulates inflammation and the production of reactive oxygen species via inhibition of S1PR2 synthesis.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2021 May;30(5):555-561. doi: 10.17219/acem/133483. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2021. PMID: 33984196
-
[Mechanism of Gegen Qinlian Decoction in improving glucose metabolism in vitro and in vivo by alleviating hepatic endoplasmic reticulum stress].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023 Oct;48(20):5565-5575. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20230516.401. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 38114149 Chinese.
References
-
- Wong TY, Sabanayagam C. Strategies to tackle the global burden of diabetic retinopathy: from epidemiology to artificial intelligence. Ophthalmologica. 2020;243(1):9–20. - PubMed
-
- Stitt AW, Curtis TM, Chen M, et al. The progress in understanding and treatment of diabetic retinopathy. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2016;51:156–186. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
