The Effect of Stem Cell Secretome on the Improvement of Diabetic Wound Recovery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of In Vivo Studies
- PMID: 40104028
- PMCID: PMC11919401
- DOI: 10.1016/j.curtheres.2025.100778
The Effect of Stem Cell Secretome on the Improvement of Diabetic Wound Recovery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of In Vivo Studies
Abstract
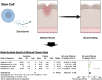
Background: Diabetic wounds, characterized by their chronic nature, represent a critical challenge for patients with diabetes, often leading to amputation and mortality. Although stem cells show great promise, their use is limited by challenges related to stability and tumorigenicity. The secretome of stem cells, comprising molecules released by these cells, offers a potential alternative to the challenges associated with stem cell therapy and provides a promising solution for diabetic wound healing.
Objective: We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of relevant preclinical studies to evaluate the effectiveness of stem cell secretomes in treating diabetic wounds.
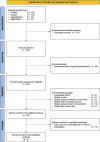
Methods: The protocol registration for this systematic review and meta-analysis was recorded in the PROSPERO database (CRD42023473726). Databases were searched from their inception until November 20, 2023. The quality assessment of the included studies was performed utilizing the CAMARADES 10-item Quality Checklist. Statistical analyses were conducted using a random-effects model to calculate standardized mean differences (SMD) and 95% confidence intervals (CI), with heterogeneity assessed via the I² statistic. The primary outcome evaluated was the wound closure rate, while secondary outcomes included parameters such as the number of fibroblasts, neutrophils, and macrophages.
Results: Twenty studies were included, comprising 382 animal subjects, and five of which were eligible for quantitative evaluation in a meta-analysis. The stem cell secretome significantly improved the wound closure rate (SMD = 9.63; 95% CI = 2.01 -17.25; P = 0.01, I2 = 76%) and reduced the number of neutrophils (SMD = -8.47; 95% CI = -13.05 to -3.90; P = 0.0003) and macrophages (SMD = -5.32; 95% CI = -9.09 to -1.55; P = 0.006).
Conclusion: This review suggests that stem cell secretomes have potential as a novel therapeutic strategy for diabetic wound healing, enhancing wound closure rates and reducing inflammation. These findings support the use of stem cell secretomes as a safer and more stable alternative to direct stem cell therapy, but further clinical studies are needed to confirm these results in human patients.
Keywords: Diabetic wound; Secretome; Stem cell; Wound healing.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
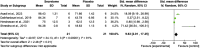




Similar articles
-
Efficacy of MSC-derived small extracellular vesicles in treating type II diabetic cutaneous wounds: a systematic review and meta-analysis of animal models.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jul 15;15:1375632. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1375632. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39076515 Free PMC article.
-
MSC-Derived Extracellular Vesicles to Heal Diabetic Wounds: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Preclinical Animal Studies.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022 Mar;18(3):968-979. doi: 10.1007/s12015-021-10164-4. Epub 2021 Apr 24. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022. PMID: 33893619 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of summer programmes on the outcomes of disadvantaged or 'at risk' young people: A systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2024 Jun 13;20(2):e1406. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1406. eCollection 2024 Jun. Campbell Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38873396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles secreted by bone marrow stem cells mediate angiogenesis for the treatment of diabetic ulcers: A systematic review and meta-analysis of preclinical studies.Heliyon. 2024 Feb 9;10(4):e25762. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25762. eCollection 2024 Feb 29. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38390125 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome on Wound Healing: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2023 Dec;20(7):1053-1062. doi: 10.1007/s13770-023-00570-9. Epub 2023 Sep 8. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2023. PMID: 37682505 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Rat Hair Follicle Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes: Isolation, Characterization and Comparative Analysis of Their In Vitro Wound Healing Potential.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 25;26(11):5081. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115081. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40507892 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

