Seasonal dynamics and molecular regulation of flavonoid biosynthesis in Cyclocarya paliurus (Batal.) Iljinsk
- PMID: 40104034
- PMCID: PMC11917369
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1525226
Seasonal dynamics and molecular regulation of flavonoid biosynthesis in Cyclocarya paliurus (Batal.) Iljinsk
Abstract
Introduction: Cyclocarya paliurus, an economically important species known for its high flavonoid content, has potential for industrial applications. Understanding the seasonal dynamics and molecular regulation of flavonoid biosynthesis in this species is crucial for optimizing its production.
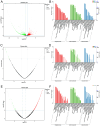
Methods: We conducted an integrated analysis of transcriptomic and metabolomic data to identify key genes involved in flavonoid biosynthesis and regulation. Seasonal variation in flavonoid content and gene expression was examined, with a focus on the genes involved in the flavonoid synthesis pathway and their correlation with flavonoid levels.
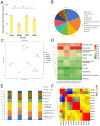
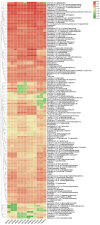
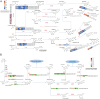
Results: Flavonoid content peaked in August and declined towards November, with quercetin and kaempferol glycosides being the most abundant compounds. Pearson correlation analysis revealed significant relationships between the functional genes of the flavonoid synthesis pathway and flavonoid content. Seasonal variations in the expression of key biosynthetic genes (CHS, CHI, F3H, DFR, FLS) and regulatory transcription factors (MYB11, MYB12, MYB111, MYB75, MYB90, bHLH, WD40) were strongly correlated with flavonoid levels, particularly under environmental stress.
Discussion: These findings provide insights into the genetic regulation of flavonoid biosynthesis in C. paliurus and highlight the importance of seasonal and environmental factors. This knowledge has practical implications for industrial breeding and biotechnological applications, particularly in enhancing the functional properties of C. paliurus for industrial use. Our study establishes a foundation for future research aimed at optimizing flavonoid production in this species and exploring its potential for bioactive compound production.
Keywords: Cyclocarya paliurus; flavonoid biosynthesis; metabolomics; seasonal variation; transcriptomics.
Copyright © 2025 Chen, Xiao, Zheng, Sun, Zhang, Zhu and Xue.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Integrated Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Analysis of the Flavonoid Accumulation in the Leaves of Cyclocarya paliurus at Different Altitudes.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Feb 8;12:794137. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.794137. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35211131 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological response and molecular regulatory mechanism reveal a positive role of nitric oxide and hydrogen sulfide applications in salt tolerance of Cyclocarya paliurus.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Sep 1;14:1211162. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1211162. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37719222 Free PMC article.
-
Light quality affects flavonoid production and related gene expression in Cyclocarya paliurus.J Photochem Photobiol B. 2018 Feb;179:66-73. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.01.002. Epub 2018 Jan 11. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2018. PMID: 29334625
-
Isolation, structure, and bioactivities of polysaccharides from Cyclocarya paliurus (Batal.) Iljinskaja.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2017 Jun;1398(1):20-29. doi: 10.1111/nyas.13357. Epub 2017 May 22. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2017. PMID: 28543531 Review.
-
Unlocking the potential of flavonoid biosynthesis through integrated metabolic engineering.Front Plant Sci. 2025 May 29;16:1597007. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1597007. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40510168 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Caowen S., Shengzuo F., Xulan S. (2023). Flavonoid biosynthesis regulation for leaf coloring of Cyclocarya paliurus . Acta Physiol. Plant 45, 91. doi: 10.1007/s11738-023-03571-2 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

