Determining the optimal antioxidant strategy: a comparative analysis of extraction methods in Cistus villosus L. extracts revealed by LC-HRMS and computational modeling
- PMID: 40104574
- PMCID: PMC11913363
- DOI: 10.55730/1300-0152.2720
Determining the optimal antioxidant strategy: a comparative analysis of extraction methods in Cistus villosus L. extracts revealed by LC-HRMS and computational modeling
Abstract
Background/aim: Cistus villosus L., a beloved tea herb, contains a treasure trove of potent antioxidants. Our research unveils this ancient ally's potential to shield against oxidative stress, a modern health threat.
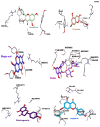
Materials and methods: Antioxidant assays were conducted to evaluate the potency of ethyl acetate extract. IC50 values were determined for the extract in various antioxidant assays. Furthermore, molecular docking was employed for the examination of the 22 compounds analyzed through LC-HRMS. Additionally, ADMET and PASS investigations were conducted to evaluate their capability as antioxidants and inhibitors of oxidant formation.
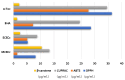
Results: Each identified compound boasts a history of antioxidant prowess, building the natural defense arsenal of C. villous. Antioxidant assays showed the potency of the ethyl acetate fraction with an IC50 value of 5.30 mg/L in the DPPH• test, which is better than that of the studied standard, α-tocopherol (36.35 mg/L). The pharmacokinetic profiles demonstrated good properties for the identified compounds. The PASS study unveiled their potential as antioxidants, and molecular docking showed their effectiveness as inhibitors of oxidant formation in the human body by blocking the studied targets.
Conclusion: This herb, a timeless testament to nature's bounty, stands poised to become a powerful weapon in our fight against oxidative stress, promising a future of natural well-being.
Keywords: Cistus villous L.; LC-HRMS; antioxidants; docking; maceration; natural health.
© TÜBİTAK.
Figures







References
-
- Abd Razak DL, Abd Ghani A, Lazim MIM, Khulidin KA, Shahidi F, et al. Schizophyllum commune (Fries) mushroom: a review on its nutritional components, antioxidative, and anti-inflammatory properties. Current Opinion in Food Science. 2024;56:101129. doi: 10.1016/j.cofs.2024.101129. - DOI
-
- Aničić N, Patelou E, Papanikolaou A, Kanioura A, Valdesturli C, et al. Comparative metabolite and gene expression analyses in combination with gene characterization revealed the patterns of flavonoid accumulation during Cistus creticus subsp. creticus fruit development. Frontiers in Plant Science. 2021;12:619634. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.619634. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
