Dietary supplement of Acanthopanax senticosus decoction formula improves immune response via intestine flora of rabbits
- PMID: 40104594
- PMCID: PMC11913833
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1508280
Dietary supplement of Acanthopanax senticosus decoction formula improves immune response via intestine flora of rabbits
Abstract
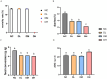
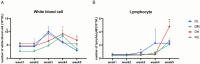
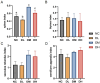
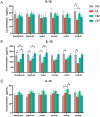
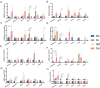
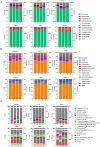
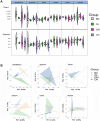
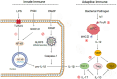
Young rabbits are sensitive to surrounding changes and conditioned pathogens in intestine which might result in slow inflammation and diarrhea after microbial invasion. Traditional medicine herbs could provide efficacious treatment on slow infection and inflammation. The present research designed an Acanthopanax senticosus (ACS) formula consisted of five types of Chinese herbs including Acanthopanax senticosus (Rupr & Maxim) Harms (Ciwujia in Chinese), Astragalus membranceus (Fisch) Bge (Huangqi in Chinese), Indigo naturalis (Qingdai in Chinese), Houttuynia cordata Thunb (Yuxingcao in Chinese), and Glycyrrhizae radix et Rhizoma (Gancao in Chinese). The effects of ACS decoction supplement were investigated via determination of cytokines and growth performances of young rabbits, and the flora in intestinal digesta from six fragments were further explored using 16S rRNA gene sequencing technology. Compared to the control group, rabbits supplied with different doses of ACS decoction possessed lower diarrhea and death rates, together with the IL-10 concentration, while the declined IL-1β and IL-12 levels and inflammatory factor gene expressions in intestinal tissues. Additionally, ACS addition changed the diversity of flora in each segments of intestine. Functional prediction on abundances of genera enriched to seven KEGG immunity pathways. Moreover, strong correlations were determined between the abundance of bacteria with interleukins contents, and the predictive immune signaling abundances, respectively. Especially, ACS exhibited anti-inflammation effects via decreasing the abundances of Bacteroides, Clostridia_vadinBB60_group, NK4A214_group, and dgA_11_gut_group in intestine of young rabbits. In conclusion, dietary supplement with ACS exerted diarrhea-reducing effects, and improved immunity homeostasis by modulating intestinal flora diversity in young rabbits.
Keywords: immunity; inflammation; intestinal flora; rabbit; traditional medicinal herbs.
Copyright © 2025 Nie, Liu, Huang, Wang, Niu and Ran.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationship that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Traditional Chinese Medicine Houttuynia cordata Thunb decoction alters intestinal barrier function via an EGFR dependent MAPK (ERK1/2) signalling pathway.Phytomedicine. 2022 Oct;105:154353. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154353. Epub 2022 Jul 27. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 35932606
-
The effects of degraded polysaccharides from Acanthopanax senticosus on growth, antioxidant and immune effects in broiler chicks based on intestinal flora.Poult Sci. 2025 Apr;104(4):104933. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.104933. Epub 2025 Feb 21. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40010047 Free PMC article.
-
[Investigating the effects of Modified Sijunzi Decoction on the diversity of intestinal microflora of severe scald rabbits based on 16S ribosomal RNA high-throughput sequencing].Zhonghua Shao Shang Yu Chuang Mian Xiu Fu Za Zhi. 2022 Mar 20;38(3):227-235. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501120-20200923-00421. Zhonghua Shao Shang Yu Chuang Mian Xiu Fu Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35325967 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
A review on the immunomodulatory activity of Acanthopanax senticosus and its active components.Chin Med. 2019 Jul 31;14:25. doi: 10.1186/s13020-019-0250-0. eCollection 2019. Chin Med. 2019. PMID: 31388349 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review of Acanthopanax senticosus (Rupr and Maxim.) harms: From ethnopharmacological use to modern application.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Mar 25;268:113586. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113586. Epub 2020 Nov 16. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33212178 Review.
References
-
- Barbosa T. N., Ferreira M. R. A., Scholl N. R., Pegoraro H. G., De Oliveira Silva M. T., Sousa F. S. S., et al. . (2024). Iridaea cordata lipid extract associated with the rCP01850 protein of C. pseudotuberculosis elicited a Th1 immune response in immunized sheep. Vaccine 42:126220. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2024.126220, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen M., Zhao Y., Li S., Chang Z., Liu H., Zhang D., et al. . (2024). Maternal malic acid may ameliorate oxidative stress and inflammation in sows through modulating gut microbiota and host metabolic profiles during late pregnancy. Antioxidants 13:253. doi: 10.3390/antiox13020253, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

