Global discovery, expression pattern, and regulatory role of miRNA-like RNAs in Ascosphaera apis infecting the Asian honeybee larvae
- PMID: 40104596
- PMCID: PMC11914139
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1551625
Global discovery, expression pattern, and regulatory role of miRNA-like RNAs in Ascosphaera apis infecting the Asian honeybee larvae
Abstract
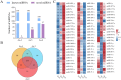
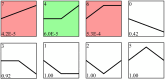
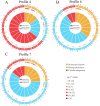
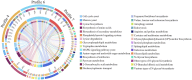
Ascosphaera apis, a specialized fungal pathogen, causes lethal infection in honeybee larvae. miRNA-like small RNAs (milRNAs) are fungal small non-coding RNAs similar to miRNAs, which have been shown to regulate fungal hyphal growth, spore formation, and pathogenesis. Based on the transcriptome data, differentially expressed miRNA-like RNAs (DEmilRNAs) in A. apis infecting the Apis cerana cerana worker 4-, 5-, and 6-day-old larvae (Aa-4, Aa-5, and Aa-6) were screened and subjected to trend analysis, followed by target prediction and annotation as well as investigation of regulatory networks, with a focus on sub-networks relative to MAPK signaling pathway, glycerolipid metabolism, superoxide dismutase, and enzymes related to chitin synthesis and degradation. A total of 606 milRNAs, with a length distribution ranging from 18 nt to 25 nt, were identified. The first nucleotide of these milRNAs presented a bias toward U, and the bias patterns across bases of milRNAs were similar in the aforementioned three groups. There were 253 milRNAs, of which 68 up-and 54 down-regulated milRNAs shared by these groups. Additionally, the expression and sequences of three milRNAs were validated by stem-loop RT-PCR and Sanger sequencing. Trend analysis indicated that 79 DEmilRNAs were classified into three significant profiles (Profile4, Profile6, and Profile7). Target mRNAs of DEmilRNAs in these three significant profiles were engaged in 42 GO terms such as localization, antioxidant activity, and nucleoid. These targets were also involved in 120 KEGG pathways including lysine biosynthesis, pyruvate metabolism, and biosynthesis of antibiotics. Further investigation suggested that DEmilRNA-targeted mRNAs were associated with the MAPK signaling pathway, glycerolipid metabolism, superoxide dismutase, and enzymes related to chitin synthesis and degradation. Moreover, the binding relationships between aap-milR10516-x and ChsD as well as between aap-milR-2478-y and mkh1 were confirmed utilizing a combination of dual-luciferase reporter gene assay and RT-qPCR. Our data not only provide new insights into the A. apis proliferation and invasion, but also lay a basis for illustrating the DEmilRNA-modulated mechanisms underlying the A. apis infection.
Keywords: Apis cerana; Ascosphaera apis; chalkbrood; milRNA; regulatory network; target mRNA.
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Geng, Ye, Xu, Zheng, Wang, Lei, Wu, Jiang, Hu, Chen, Yan, Guo and Qiu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Transcriptional dynamics and regulatory function of milRNAs in Ascosphaera apis invading Apis mellifera larvae.Front Microbiol. 2024 Apr 8;15:1355035. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1355035. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38650880 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic Characterization of miRNAs in Apis cerana Larvae Responding to Ascosphaera apis Infection.Genes (Basel). 2025 Jan 26;16(2):156. doi: 10.3390/genes16020156. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40004485 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory Roles of Long Non-Coding RNAs Relevant to Antioxidant Enzymes and Immune Responses of Apis cerana Larvae Following Ascosphaera apis Invasion.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 16;24(18):14175. doi: 10.3390/ijms241814175. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762477 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics and regulatory role of circRNAs in Asian honey bee larvae following fungal infection.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Mar 13;108(1):261. doi: 10.1007/s00253-024-13102-9. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38472661 Free PMC article.
-
Trans-Kingdom RNA Dialogues: miRNA and milRNA Networks as Biotechnological Tools for Sustainable Crop Defense and Pathogen Control.Plants (Basel). 2025 Apr 20;14(8):1250. doi: 10.3390/plants14081250. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40284138 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Asl E. R., Amini M., Najafi S., Mansoori B., Mokhtarzadeh A., Mohammadi A., et al. . (2021). Interplay between MAPK/ERK signaling pathway and MicroRNAs: a crucial mechanism regulating cancer cell metabolism and tumor progression. Life Sci. 278:119499. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119499, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

