Recent advances in bioactive hydrogel microspheres: Material engineering strategies and biomedical prospects
- PMID: 40104647
- PMCID: PMC11919335
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.101614
Recent advances in bioactive hydrogel microspheres: Material engineering strategies and biomedical prospects
Abstract
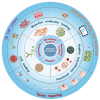
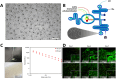
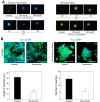
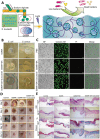
Hydrogel microspheres are a class of hydrophilic polymeric particles in microscale, which has been developed as a new type of functional biomaterials for wide-range biomedical applications in recent years. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the preparation methods for hydrogel microspheres, including droplet microfluidics, electrospray and emulsion was first summarized. At the same time, we analyze the impacts of these methods on the properties of hydrogel microspheres and explore various functionalization strategies for enhancing their bioactivity and expanding their biomedical applications. In addition, we discuss the recent advances and the further prospect of hydrogel microspheres in life science applications, particularly in cell biology research, bioanalysis and detection, as well as tissue repair and regeneration. By synthesizing the latest developments, this review aims to offer valuable insights and strategies for optimizing hydrogel microspheres in diverse application scenarios and inspire future research and practical innovations.
Keywords: 3D cell culture; Biofunctionalization; Biosensing; Hydrogel microspheres; Microfluidics; Tissue regeneration.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures









References
-
- Zhang Q., Wei X., Ji Y., Yin L., Dong Z., Chen F., Zhong M., Shen J., Liu Z., Chang L. Adjustable and ultrafast light-cured hyaluronic acid hydrogel: promoting biocompatibility and cell growth. J. Mater. Chem. B. 2020;8:5441–5450. http://10.1039/c9tb02796c - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhou D., Li S., Pei M., Yang H., Gu S., Tao Y., Ye D., Zhou Y., Xu W., Xiao P. vol. 12. 2020. pp. 18225–18234.http://10.1021/acsami.9b22120 (Dopamine-Modified Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel Adhesives with Fast-Forming and High Tissue Adhesion). - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bian J., Cai F., Chen H., Tang Z., Xi K., Tang J., Wu L., Xu Y., Deng L., Gu Y., Cui W., Chen L. Modulation of local overactive inflammation via injectable hydrogel microspheres. Nano Lett. 2021;21:2690–2698. http://10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c04713 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sagar Prem, Handa Amit, Kumar Gitesh, Gupta Vikas, Walia Rinku, Singla S. Nanocomposite hydrogel materials for defective cartilage repair and its mechanical tribological behavior-A review. Pap. Biomater. 2022;7:63–72. http://10.1213/j.issn.2096-2355.2022.03.007 - DOI
-
- X. Chen, X. Li, W. He, M. Wang, A. Gao, L. Tong, S. Guo, H. Wang, G. Pan,Rational multivalency construction enables bactericidal effect amplification and dynamic biomaterial design. Innovation, 4 100483.http://10.1016/j.xinn.2023.100483. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

