Narrative review of 3D bioprinting for the construction of in vitro tumor models: present and prospects
- PMID: 40104735
- PMCID: PMC11912033
- DOI: 10.21037/tcr-2025-128
Narrative review of 3D bioprinting for the construction of in vitro tumor models: present and prospects
Abstract
Background and objective: The conventional in vitro research on tumor mechanisms is typically based on two-dimensional (2D) culture of tumor cells, which has many limitations in replicating in vivo tumorigenesis processes. In contrast, the three-dimensional (3D) bioprinting has paved the way for the construction of more biomimetic in vitro tumor models. This article comprehensively elucidates the features of 3D bioprinting and meticulously summarizes its applications in several selected tumors, aiming to offer valuable insights for future relevant studies.
Methods: A literature search was conducted in the databases of PubMed and Web of Science for articles on 3D bioprinting for in vitro tumor model construction.
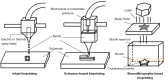
Key content and findings: This article introduces various 3D bioprinting technologies for in vitro tumor model construction, focusing on their pros and cons, principles, and protocols. Several in vitro tumor models are presented, detailing their utility in tumorigenesis research and their constraints. To date, 3D bioprinting has been widely applied in oncology, addressing the limitation of traditional 2D tumor cell culture in replicating tumor microenvironment (TME).
Conclusions: Advanced 3D bioprinting technology accurately replicates the complex TME and the heterogeneity of intratumor structures, enabling further in vitro tumor studies. It significantly fuels our understanding of tumor pathophysiology and offers new hope for cancer patients.
Keywords: Bioprinting; in vitro tumor models; tumor microenvironment (TME).
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tcr-2025-128/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
3D Bioprinting for In Vitro Models of Oral Cancer: Toward Development and Validation.Bioprinting. 2021 Jun;22:e00132. doi: 10.1016/j.bprint.2021.e00132. Bioprinting. 2021. PMID: 34368488 Free PMC article.
-
Narrative review of gene modification: applications in three-dimensional (3D) bioprinting.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Oct;9(19):1502. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-2854. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34805364 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spheroid-Hydrogel-Integrated Biomimetic System: A New Frontier in Advanced Three-Dimensional Cell Culture Technology.Cells Tissues Organs. 2025;214(2):128-147. doi: 10.1159/000541416. Epub 2024 Sep 12. Cells Tissues Organs. 2025. PMID: 39265553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
3D Bioprinting: An Important Tool for Tumor Microenvironment Research.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 Dec 28;18:8039-8057. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S435845. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 38164264 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mimicking tumor microenvironment by 3D bioprinting: 3D cancer modeling.Biofabrication. 2022 May 31;14(3). doi: 10.1088/1758-5090/ac6d11. Biofabrication. 2022. PMID: 35512666 Review.
Cited by
-
Revolutionizing cancer care: Bioprinting prostate cancer stem cells for targeted treatments.World J Clin Oncol. 2025 Jul 24;16(7):107007. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i7.107007. World J Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40741183 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Medulloblastoma: biology and immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 3;16:1602930. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1602930. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40677711 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Samavedi S, Joy N. 3D printing for the development of in vitro cancer models. Current Opinion in Biomedical Engineering 2017;2:35-42.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
