Construction and validation of a prognostic model of lncRNAs associated with RNA methylation in lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 40104741
- PMCID: PMC11912078
- DOI: 10.21037/tcr-24-1085
Construction and validation of a prognostic model of lncRNAs associated with RNA methylation in lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Background: Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) is a common type of lung cancer and one of the leading causes of cancer death worldwide. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) play a crucial role in tumors. The purpose of this study was to explore the expression of lncRNAs associated with RNA methylation modification and their prognostic value in LUAD.
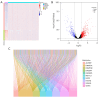
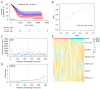
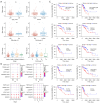
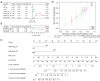
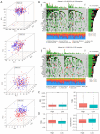
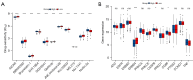
Methods: The RNA sequencing and clinical data were downloaded from The Cancer Genome Atlas dataset, and the messenger RNA and lncRNAs were annotated by Ensemble. The lncRNAs related to RNA methylation regulators (RMlncRNAs) were filtered by Pearson correlation analysis between differentially expressed lncRNAs and RNA methylation regulators. Univariate Cox regression analysis, multivariate Cox regression analysis, and least absolute shrinkage and selection operator regression analysis were used to construct a prognostic model. The receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) was plotted to validate the predictive value of the prognostic model. Then, tumor mutational burden (TMB) and microsatellite instability were used to compare the immunotherapy response. Finally, to perform a drug sensitivity analysis, the half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of targeted drugs was calculated using pRRophetic package.
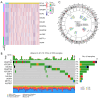
Results: In total, 18 RMlncRNAs associated with the prognosis of LUAD patients were identified. Then, six feature lncRNAs (NFYC-AS1, OGFRP1, MIR4435-2HG, TDRKH-AS1, DANCR, and TMPO-AS1) were used to construct a prognostic model. The ROC curves for training, testing, and validation sets showed that the prognosis model was effective. The subindex based on the prognostic model had a high correlation with TMB. The high-risk group might be subject to greater immune resistance according to the comparison of Tumor Immune Dysfunction and Exclusion scores. Finally, the IC50 of 11 drugs had differences between high- and low-risk group, and only three of the drug's target genes (ERBB4, CASP8, and CD86) were differentially expressed.
Conclusions: In conclusion, a prognostic model based on six feature lncRNAs (NFYC-AS1, OGFRP1, MIR4435-2HG, TDRKH-AS1, DANCR, and TMPO-AS1) was constructed by bioinformatics analysis, which might provide a new insight into the evaluation and treatment of LUAD.
Keywords: Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs); RNA methylation regulators; immunotherapy response; prognostic model.
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tcr-24-1085/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification and validation of an autophagy-related long non-coding RNA signature as a prognostic biomarker for patients with lung adenocarcinoma.J Thorac Dis. 2021 Feb;13(2):720-734. doi: 10.21037/jtd-20-2803. J Thorac Dis. 2021. PMID: 33717544 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-talk between necroptosis-related lncRNAs to construct a novel signature and predict the immune landscape of lung adenocarcinoma patients.Front Genet. 2022 Sep 15;13:966896. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.966896. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36186456 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of RNA Methylation Modification-immune-related lncRNA Molecular Subtypes and Prognostic Scoring System in Lung Adenocarcinoma.Curr Med Chem. 2024;31(12):1539-1560. doi: 10.2174/0929867331666230901110629. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 37680151
-
Prognostic signature of lipid metabolism associated LncRNAs predict prognosis and treatment of lung adenocarcinoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 1;12:986367. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.986367. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36387240 Free PMC article.
-
A cuproptosis-related long non-coding RNA signature to predict the prognosis and immune microenvironment characterization for lung adenocarcinoma.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2022 Oct;11(10):2079-2093. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-22-660. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 36386454 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
