A novel necroptosis-related miRNA signature for predicting the prognosis of esophageal cancer and immune infiltration analysis
- PMID: 40104746
- PMCID: PMC11912044
- DOI: 10.21037/tcr-24-1532
A novel necroptosis-related miRNA signature for predicting the prognosis of esophageal cancer and immune infiltration analysis
Abstract
Background: The prognostic value of necroptosis-related microRNAs (miRNAs), which are important in tumorigenesis and development, remains unclear. Therefore, we aimed to screen prognostic necroptosis-related miRNAs in esophageal cancer (EC).
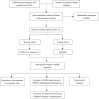
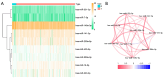
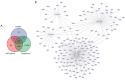
Methods: Nine necroptosis-related miRNA expression profiles and associated clinical data of EC patients were obtained from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. The relationships between necroptosis-related miRNAs and overall survival (OS) were determined via Cox regression model analysis. Target genes of the miRNAs were investigated in TargetScan, miRDB, and miRTarBase. The biological functions of these genes were evaluated by Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analyses. For the most significant correlation between miR-425-5p expression and the survival of EC patients, the effect of miR-425-5p on necroptosis was explored in EC cells. The relationship between targeted gene expression and immune infiltration was also analyzed and validated.
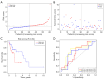
Results: Hsa-miR-425-5p, hsa-miR-500a-3p, hsa-miR-7-5p and hsa-miR-200a-5p were selected for the construction of a prognostic signature based on their correlation with the survival of EC patients. EC patients were divided into high- and low-risk groups according to the median value of the risk score. Patients in the high-risk group tended to have higher death rates than those in the low-risk group (P<0.05). The risk score was an independent prognostic indicator for the OS of EC patients [hazard ratio (HR) >1, P<0.05]. The prognostic model had good predictive efficiency. The genes targeted by necroptosis-related miRNAs were significantly enriched in apoptosis etc. The inhibition of miR-425-5p promoted necroptosis in EC cells by targeting branched chain amino acid transaminase 1 (BCAT1). The expression level of BCAT1 was significantly correlated with immune infiltration.
Conclusions: A necroptosis-related four-miRNA model was constructed successfully to predict the potential value of the four miRNAs in the prognosis of EC, which can be conducive to promoting the therapeutic effect on EC.
Keywords: Esophageal cancer (EC); miRNA signature; necroptosis; prognosis.
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tcr-24-1532/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A novel necroptosis-associated miRNA signature predicting prognosis of endometrial cancer and correlated with immune infiltration.Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2023 Mar;62(2):291-298. doi: 10.1016/j.tjog.2022.09.009. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2023. PMID: 36965898
-
Development of a necroptosis-related prognostic model for uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 21;14(1):4257. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-54651-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38383747 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Necroptosis-Related miRNA Signature for Predicting the Prognosis of Breast Cancer Metastasis.Dis Markers. 2022 Mar 25;2022:3391878. doi: 10.1155/2022/3391878. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 35371342 Free PMC article.
-
A novel prognostic signature for clear cell renal cell carcinoma constructed using necroptosis-related miRNAs.BMC Genomics. 2023 Mar 29;24(1):162. doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09258-9. BMC Genomics. 2023. PMID: 36991314 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering the role of microRNAs in esophageal cancer: from pathogenesis to clinical applications.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 29;16:1532558. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1532558. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39944625 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Urinary microRNAs as Prognostic Biomarkers for Predicting the Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Patients with Urothelial Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Aug 13;17(16):2640. doi: 10.3390/cancers17162640. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40867269 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
