The miR-155-5p/ FBXO11 axis inhibits the progression of gastric cancer via the mTOR pathway
- PMID: 40104748
- PMCID: PMC11912068
- DOI: 10.21037/tcr-2025-8
The miR-155-5p/ FBXO11 axis inhibits the progression of gastric cancer via the mTOR pathway
Abstract
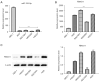
Background: Gastric cancer (GC) is a leading cause of cancer-related death. MicroRNAs (miRNAs or miRs) play a crucial role in the pathology of GC, including cell proliferation, invasion, and metastasis. In this study, genes targeted by miR-155-5p were predicted using bioinformatic tools. We found that the expression of miR-155-5p in GC cell lines differed relative to the expression of F-box protein 11 (FBXO11), which is involved in the regulation of cellular processes. This study sought to examine the function of miR-155-5p and the precise mechanism underlying its regulatory function in modulating proliferation and apoptosis in GC.
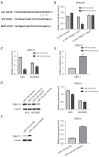
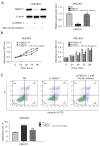
Methods: The luciferase reporter assay results showed that miR-155-5p bound directly to the three prime untranslated region (3'-UTR) of FBXO11, which further downregulated FBXO11 expression. Quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and Western-blot analyses confirmed that miR-155-5p negatively regulated the messenger RNA (mRNA) and protein expression of FBXO11. The effects of FBXO11 on cell proliferation and apoptosis in GC cell lines was further examined using Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) and flow cytometry.
Results: We found that FBXO11 promoted proliferation and decreased apoptosis in GC cells. Conversely, rescue experiments showed that the knockdown of FBXO11 limited the effects of miR-155-5p on the proliferation and apoptosis of GC cells, providing further evidence that FBXO11 is a functional target of miR-155-5p. Further, the overexpression of miR-155-5p inhibited cell growth via the targeted inhibition of FBXO11 that regulated mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway in the GC cells.
Conclusions: Overall, these results showed that miR-155-5p may serve as a tumor suppressor in GC and that the miR-155-5p/FBXO11 axis regulates tumor progression via the mTOR signaling pathway. Consequently, our findings may lead to the development a novel treatment strategy for GC.
Keywords: FBXO11; Gastric cancer (GC); mammalian target of rapamycin pathway (mTOR pathway); miR-155-5p; proliferation.
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tcr-2025-8/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
miR-181a-5p inhibits the proliferation and invasion of drug-resistant glioblastoma cells by targeting F-box protein 11 expression.Oncol Lett. 2020 Nov;20(5):235. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.12098. Epub 2020 Sep 14. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32968457 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of miR-584-5p inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis by targeting WW domain-containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1 in gastric cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Apr 21;36(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s13046-017-0532-2. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28431583 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-129-5p inhibits proliferation of gastric cancer cells through targeted inhibition on HMGB1 expression.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020 Apr;24(7):3665-3673. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202004_20829. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32329842
-
MiRNA-145-5p inhibits gastric cancer progression via the serpin family E member 1- extracellular signal-regulated kinase-1/2 axis.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 May 15;16(5):2123-2140. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i5.2123. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38764835 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA KCNQ1OT1 promotes the progression of gastric cancer via the miR-145-5p/ARF6 axis.J Gene Med. 2021 May;23(5):e3330. doi: 10.1002/jgm.3330. Epub 2021 Apr 6. J Gene Med. 2021. Retraction in: J Gene Med. 2024 Aug;26(8):e3727. doi: 10.1002/jgm.3727. PMID: 33682985 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
