Pediococcus pentosaceus JS35 improved flavor, metabolic profile of fermentation supernatant of mulberry leaf powder and increased its antioxidant capacity
- PMID: 40104817
- PMCID: PMC11913688
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1551689
Pediococcus pentosaceus JS35 improved flavor, metabolic profile of fermentation supernatant of mulberry leaf powder and increased its antioxidant capacity
Abstract
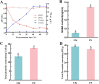
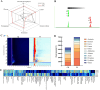
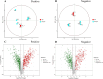
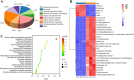
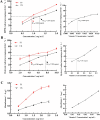
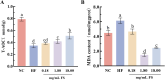
Pediococcus pentosaceus JS35 was used to improve flavor, metabolic profile and antioxidant activity of mulberry leaf powder. Gas chromatography ion mobility spectrometry (GC-IMS) analysis revealed that fermentation increased the contents of floral and fruity flavor compounds such as dihydrolinalool and 2-phenylethanol, while decreased the grassy, pungent odor compounds. Non-targeted metabolomics analysis showed that Pediococcus pentosaceus JS35 altered the metabolic profile of mulberry leaf, especially increased the content of flavonoids metabolites such as kaempferol, quercetin and daidzein. Compared with the unfermented sample, the fermented supernatant had higher antioxidant capacity in vitro and in Caenorhabditis elegans. Furthermore, the fermented supernatant supplementation significantly prolonged the lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans. In conclusion, fermentation by Pediococcus pentosaceus JS35 improved the flavor and active compounds of mulberry leaf, and the fermented product had effective antioxidant capacity. This study will provide ideas for the application of Pediococcus pentosaceus JS35 and the processing of mulberry leaf into functional foods or food ingredient.
Keywords: Pediococcus pentosaceus; antioxidant capacity; flavor; metabolic profiles; mulberry leaf.
Copyright © 2025 Meng, Wang, Xie, Xuan, Geng, Liu, Tu and Xiao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Fermentation of Pediococcus pentosaceus JC30 Improves Phytochemical, Flavor Characteristics and Antioxidant Activity of Mulberry Leaves.Molecules. 2025 Apr 10;30(8):1703. doi: 10.3390/molecules30081703. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40333611 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of fermentation by Pediococcus pentosaceus and Staphylococcus carnosus on the metabolite profile of sausages.Food Res Int. 2022 Dec;162(Pt B):112096. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.112096. Epub 2022 Nov 2. Food Res Int. 2022. PMID: 36461402
-
Chemical characteristics, antioxidant capacity, bacterial community, and metabolite composition of mulberry silage ensiling with lactic acid bacteria.Front Microbiol. 2024 Apr 8;15:1363256. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1363256. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38650879 Free PMC article.
-
Pediococcus pentosaceus: Screening and Application as Probiotics in Food Processing.Front Microbiol. 2021 Dec 16;12:762467. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.762467. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34975787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pediococcus pentosaceus, a future additive or probiotic candidate.Microb Cell Fact. 2021 Feb 16;20(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s12934-021-01537-y. Microb Cell Fact. 2021. PMID: 33593360 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolic Variations in Bamboo Shoot Boiled Liquid During Pediococcus pentosaceus B49 Fermentation.Foods. 2025 Aug 5;14(15):2731. doi: 10.3390/foods14152731. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40807668 Free PMC article.
-
Moderate Ohmic Field Modification of Okara and Its Effects on Physicochemical Properties, Structural Organization, and Functional Characteristics.Foods. 2025 May 21;14(10):1833. doi: 10.3390/foods14101833. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40428612 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

