[Factors associated with prognosis and treatment failure in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia]
- PMID: 40105076
- PMCID: PMC11928036
- DOI: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2409008
[Factors associated with prognosis and treatment failure in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia]
Abstract
Objectives: To explore the factors related to prognosis and treatment failure in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).
Methods: A retrospective study was conducted to collect and analyze clinical data of ALL children admitted to the Department of Pediatric Hematology at Tongji Hospital, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, from January 2012 to December 2019, with follow-up until June 2024.
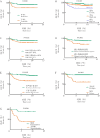
Results: A total of 341 children with ALL were included. Among the 69 children with treatment failure, 55 (80%) experienced relapse, while 14 (20%) had non-relapse-related deaths, and no secondary tumors were observed. Initial WBC count ≥50×109/L, positive minimal residual disease, and severe adverse events were identified as independent risk factors for treatment failure (P<0.05). Among the 55 relapsed patients, early relapses were predominant (36%), and the primary site of relapse was the bone marrow (56%). Immunophenotyping (P=0.009), initial WBC count (P=0.011), and fusion genes (P=0.040) were associated with the timing of relapse. High-risk status, T-cell ALL, relapse, and severe adverse events were independent risk factors affecting long-term survival (P<0.05).
Conclusions: The prognosis of children with ALL is related to risk stratification, immunophenotyping, relapse status, and occurrence of severe adverse events. Among these factors, relapse is the primary cause of treatment failure. Actively preventing relapse may reduce the treatment failure rate and improve long-term survival.
目的: 分析急性淋巴细胞白血病(acute lymphoblastic leukemia, ALL)儿童的预后及治疗失败的相关因素。方法: 回顾性收集并研究华中科技大学同济医学院附属同济医院儿童血液科2012年1月—2019年12月收治的ALL患儿的临床资料,随访至2024年6月。结果: 共纳入341例ALL患儿。69例治疗失败患儿中,复发55例(80%),非复发性死亡14例(20%),无患儿发生二次肿瘤;初诊WBC计数≥50×109/L、微小残留病灶阳性及严重不良事件是治疗失败的独立危险因素(P<0.05);55例复发患儿中,复发时间以极早期复发为主(36%),复发部位以骨髓复发为主(56%),免疫分型(P=0.009)、初诊WBC计数(P=0.011)及融合基因(P=0.040)与复发时间有关;高危、T细胞ALL、复发及严重不良事件是影响ALL儿童长期生存率的独立危险因素(P<0.05)。结论: ALL儿童预后与危险分层、免疫分型、是否复发及是否发生严重不良事件等因素相关,其中复发是患儿治疗失败的主要原因,积极预防复发可降低患儿的治疗失败率,提高长期生存率。.
Keywords: Acute lymphoblastic leukemia; Child; Prognosis; Risk factor; Treatment failure.
Conflict of interest statement
所有作者声明无任何利益冲突。
Figures
Similar articles
-
[The Factors Related to Treatment Failure in Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia].Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2021 Jun;29(3):661-668. doi: 10.19746/j.cnki.issn.1009-2137.2021.03.002. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34105454 Chinese.
-
[The Factors Related to Treatment Failure in Children with Acute Lymphoblastic leukemia--Analysis of Multi-Center Data from Real World in Fujian Province].Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Dec;32(6):1656-1664. doi: 10.19746/j.cnki.issn.1009-2137.2024.06.005. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39743248 Chinese.
-
[Clinical features and long-term prognostic analysis of relapsed pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2024 Nov 2;62(11):1090-1096. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112140-20240914-00643. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39429082 Chinese.
-
Low relapse rate in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia after risk-directed therapy.J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2001 Dec;23(9):591-7. doi: 10.1097/00043426-200112000-00008. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2001. PMID: 11902303 Review.
-
[Therapeutic strategies for childhood high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2013 Apr 18;45(2):327-32. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2013. PMID: 23591360 Review. Chinese.
References
-
- 张之南, 沈悌. 血液病诊断及疗效标准[M]. 3版. 北京: 科学出版社, 2007: 116-121.
-
- Elitzur S, Izraeli S. Pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia[J]. Harefuah, 2023, 162(1): 57-63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources