Leadless pacing: a comprehensive review
- PMID: 40105878
- PMCID: PMC12127730
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaf119
Leadless pacing: a comprehensive review
Abstract
Over the past decade, leadless pacing has undergone a rapid evolution, resulting in multiple leadless pacemaker (LPM) devices that offer advancements such as atrioventricular synchronized pacing in VDD mode, atrial stimulation, dual-chamber pacing, and longer battery longevity. Studies comparing LPMs with transvenous pacemakers (TVPMs) show a lower rate of device-related complications with LPMs. In the near future, LPMs could be combined with other devices such as non-transvenous implantable cardioverter-defibrillators to provide anti-tachycardia pacing or bradycardia pacing. Future prospectives for leadless cardiac resynchronization therapy and leadless conduction system pacing are being investigated. As LPMs continue to improve, their applications are anticipated to expand further improving patient outcome, promising a bright future for leadless pacing. In this review, the past, present, and future of leadless pacing are discussed with a focus on cutting-edge implantation techniques, clinical outcomes, and modern advancements of LPMs.
Keywords: AVEIR; CRT; CSP; Leadless pacemaker; Micra.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures

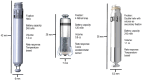
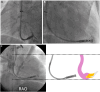
References
-
- Altman LK. Arne H. W. Larsson, 86; Had first internal pacemaker. The New York Times, 18 January 2002, Sect. C.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

