The Use of Deep Eutectic Solvents for the Synthesis of Iron Oxides Nanoparticles: A Driving Force for Materials Properties
- PMID: 40105897
- PMCID: PMC12057613
- DOI: 10.1002/chem.202500089
The Use of Deep Eutectic Solvents for the Synthesis of Iron Oxides Nanoparticles: A Driving Force for Materials Properties
Abstract
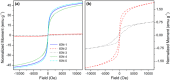
In this study, we explored the use of Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) as a green and sustainable alternative for the synthesis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (IONs). Six different binary mixtures of Hydrogen Bond Acceptors (HBAs) and Donors (HBDs) were prepared and thoroughly characterized to investigate how their components and physicochemical properties influence the structure, morphology, and magnetic properties of the resulting IONs. In addition, the role of DESs was assessed using ATR-MIR spectroscopy, providing insights into HBA-HBD interactions with iron precursors. The study highlights the critical role of DES constituents, particularly the interactions between HBAs and HBDs, in directing nanoparticle size, structure, and morphology. Indeed, our results demonstrate that the choice of DES significantly impacts the crystalline phase of iron oxide nanoparticles, yielding either magnetite (Fe₃O₄) or hematite (α-Fe₂O₃). These findings established a robust framework for leveraging DES in nanomaterial synthesis, paving the way for more environmentally friendly approaches in diverse industrial and scientific applications.
Keywords: Deep Eutectic Solvents; Hematite; IONs; Magnetite; Structural oriented synthesis.
© 2025 The Author(s). Chemistry – A European Journal published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
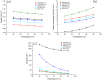
 ), ChCl:TEG (1:3) (
), ChCl:TEG (1:3) ( ), ChCl:U (1:2) (
), ChCl:U (1:2) ( ), GC:TEG (1:2) (
), GC:TEG (1:2) ( ), and GC:U (1:2) (
), and GC:U (1:2) ( ).
).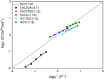
 ), ChCl:TEG (1:3) (
), ChCl:TEG (1:3) ( ), ChCl:U (1:2) (
), ChCl:U (1:2) ( ), GC:TEG (1:3) (
), GC:TEG (1:3) ( ), and GC:U (1:2)ChCl:GA (3:1) (
), and GC:U (1:2)ChCl:GA (3:1) ( ); the black straight line is referred to a 0.1 M solution of KCl.
); the black straight line is referred to a 0.1 M solution of KCl.
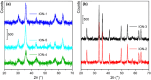
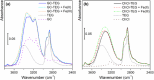
 ), in interaction with FeCl2∙4H2O (
), in interaction with FeCl2∙4H2O ( ), and in interaction with FeCl3∙6H2O (
), and in interaction with FeCl3∙6H2O ( ). Part (b): ATR‐MIR spectra (normalized with respect to the 1060 cm−1 peak of TEG) of ChCl:TEG (1:3) alone (∙), in interaction with FeCl2∙4H2O (
). Part (b): ATR‐MIR spectra (normalized with respect to the 1060 cm−1 peak of TEG) of ChCl:TEG (1:3) alone (∙), in interaction with FeCl2∙4H2O ( ), and in interaction with FeCl3∙6H2O (
), and in interaction with FeCl3∙6H2O ( ). Dotted curves are referred to DES components, namely TEG (
). Dotted curves are referred to DES components, namely TEG ( ), GC (
), GC ( ), and ChCl (
), and ChCl ( ). Full spectra are reported in Figure S6.
). Full spectra are reported in Figure S6.References
-
- a) Lu A. H., Salabas E. L., Schüth F., Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1222. - PubMed
- b) Selim M. M., El‐Safty S., Tounsi A., Shenashen M., APL Mater. 2024, 12, 010601.
- c) Ali A., Shah T., Ullah R., Zhou P. F., Guo M. L., Ovais M., Tan Z. Q., Rui Y. K., Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 629054. - PMC - PubMed
- d) Indira T. K., Lakshmi P. K., Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Nanotechnol. 2010, 3, 1035.
- e) Mohammed L., Gomaa H. G., Ragab D., Zhu J., Particuology 2017, 30, 1.
- f) Rezaei B., Yari P., Sanders S. M., Wang H. T., Chugh V. K., Liang S., Mostufa S., Xu K. L., Wang J. P., Gómez‐Pastora J., Wu K., Small 2024, 20, 2304848. - PubMed
- g) Zhang K., Song X. L., Liu M., Chen M. H., Li J., Han J. L., Water 2023, 15, 3077.
-
- a) Lazzarini A., Colaiezzi R., Galante A., Passacantando M., Capista D., Ferella F., Alecci M., Crucianelli M., Results Chem. 2022, 4, 100387.
- b) Gupta A. K., Wells S., IEEE Trans. Nanobiosci. 2004, 3, 66. - PubMed
- c) Anik M. I., Hossain M. K., Hossain I., Mahfuz A., Rahman M. T., Ahmed I., Nano Sel. 2021, 2, 1146.
- d) Persigehl T., Bieker R., Matuszewski L., Wall A., Kessler T., Kooijman H., Meier N., Ebert W., Berdel W. E., Heindel W., Mesters R. M., Bremer C., Radiology 2007, 244, 449. - PubMed
- e) Nelson N. R., Port J. D., Pandey M. K., J. Nanotheranostics 2020, 1, 105.
-
- a) Prucek R., Tucek J., Kilianová M., Panácek A., Kvítek L., Filip J., Kolár M., Tománková K., Zboril R., Biomaterials 2011, 32, 4704. - PubMed
- b) Nosrati H., Salehiabar M., Davaran S., Ramazani A., Manjili H. K., Danafar H., Res. Chem. Intermed. 2017, 43, 7423.
- c) Quan K. C., Zhang Z. X., Chen H., Ren X. X., Ren Y. J., Peterson B. W., van der Mei H. C., Busscher H. J., Small 2019, 15, 1902313. - PubMed
-
- a) Jin Y. J., Liu F., Shan C., Tong M. P., Hou Y. L., Water Res. 2014, 50, 124. - PubMed
- b) Kilianová M., Prucek R., Filip J., Kolarík J., Kvítek L., Panácek A., Tucek J., Zboril R., Chemosphere 2013, 93, 2690. - PubMed
- c) Mushtaq F., Chen X. Z., Torlakcik H., Steuer C., Hoop M., Siringil E. C., Marti X., Limburg G., Stipp P., Nelson B. J., Pané S., Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1901378. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- (CUP: E13C22001060006)/European Union - NextGenerationEU under the Italian Ministry of University and Research (MUR) National Innovation Ecosystem ECS00000041 - VITALITY
- (SCN_00520)/Italian Ministry of Education, Universities and Research (MIUR) - Smart Cities and Communities and Social Innovation on Cultural Heritage
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

