Reverse shoulder arthroplasty for proximal humerus fracture: does tuberosity reinsertion improve the functional outcomes more than 5 years after surgery?
- PMID: 40106028
- PMCID: PMC11923004
- DOI: 10.1007/s00590-025-04227-2
Reverse shoulder arthroplasty for proximal humerus fracture: does tuberosity reinsertion improve the functional outcomes more than 5 years after surgery?
Abstract
Introduction: While tuberosity reinsertion significantly improves the short-term functional outcomes of reverse shoulder arthroplasty done for proximal humerus fracture, we do not know how well these results hold over the long term. The objective of this study was to analyze the effect of tuberosity reinsertion on the quality of life of patients and the functional outcomes of the operated limb after a minimum follow-up of 5 years.
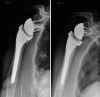
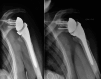
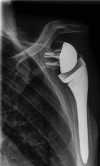
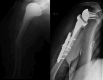
Methods: Sixty-two patients were included. Their mean age at the final review was 79 ± 10 years. The Katz and Lawton scales, Constant score, DASH and SSV were collected. Radiographs were made at the final assessment to analyze the position of the tuberosities and to look for radiological signs of implant loosening.
Results: The mean follow-up was 6.7 ± 1.5 years. The tuberosities had been reinserted in 35 patients (56%). There were no statistically significant differences between groups in the Katz (p = 0.60) and Lawton (p = 0.49) scales, nor the DASH (p = 0.45) or SSV (p = 0.49) at the final review. The Constant score was significantly better in the patients who had their tuberosities reinserted (p = 0.01), also the active forward flexion (p = 0.02), the internal rotation (p = 0.01), and the external rotation arm abduction (p = 0.02), but there was no significant difference for external rotation elbow at side (p = 0.14). None of the patients underwent revision surgery for implant loosening.
Conclusion: Tuberosity reinsertion has a functional benefit beyond 5 years postoperative, although it does not appear to have a significant effect on the geriatric outcomes or the subjective clinical scores. The patients regained satisfactory independence for an orthogeriatric population.
Level of evidence: Level IV-Retrospective study.
Keywords: Constant score; Geriatric evaluation; Reverse shoulder arthroplasty; Tuberosities.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest related directly to this work. Outside this study: MS: Associate Editor for Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research, Consulting for Quanta Medical VCLS™ and Cousin Surgery™. Generative AI and AI-assisted technologies in the writing process: No artificial intelligence software was used.
Figures
References
-
- Roux A, Decroocq L, El Batti S, Bonnevialle N, Moineau G, Trojani C, Boileau P, De Peretti F (2012) Epidemiology of proximal humerus fractures managed in a trauma center. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 98:715–719. 10.1016/j.otsr.2012.05.013 - PubMed
-
- Palvanen M, Kannus P, Niemi S, Parkkari J (2006) Update in the epidemiology of proximal humeral fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res 442:87–92. 10.1097/01.blo.0000194672.79634.78 - PubMed
-
- Bonnevialle N, Tournier C, Clavert P, Ohl X, Sirveaux F, Saragaglia D et al (2016) Hemiarthroplasty versus reverse shoulder arthroplasty in 4-part displaced fractures of the proximal humerus: multicenter retrospective study. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res OTSR 102:569–573. 10.1016/j.otsr.2016.02.014 - PubMed
-
- Gallinet D, Ohl X, Decroocq L, Dib C, Valenti P, Boileau P (2018) Is reverse total shoulder arthroplasty more effective than hemiarthroplasty for treating displaced proximal humerus fractures in older adults? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 104:759–766 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

