MiR-101-3p targets the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway via Birc5 to inhibit invasion, proliferation, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 40106068
- PMCID: PMC11923034
- DOI: 10.1007/s10238-025-01622-1
MiR-101-3p targets the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway via Birc5 to inhibit invasion, proliferation, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
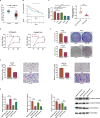
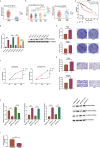
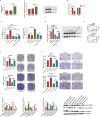
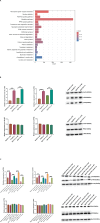
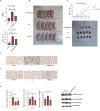
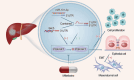
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNA molecules that regulate numerous genes in cells. Abnormal expression of miRNAs can lead to cancer. However, the roles and underlying mechanisms of miRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) are not fully understood. Using molecular biology techniques, we designed eukaryotic expression vectors with enhanced expression of miR-101-3p to transfect human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Subsequent to this, cell cloning experiments, CCK8 assays, and Transwell migration experiments were executed to assess their impact on liver cancer cell proliferation and invasion. Dual-luciferase assays were employed to validate the molecular interaction between miR-101-3p and Birc5. Through rescue experiments aimed at manipulating the expression levels of Birc5, we scrutinized the influence of miR-101-3p on liver cancer cell proliferation and invasion. Furthermore, Western blot analysis was utilized to monitor alterations in the expression levels of E-cadherin, N-cadherin, and vimentin proteins within each cell group. In vivo investigations were conducted using nude mice implanted with hepatocellular carcinoma cells transfected with Birc5. Additionally, further exploration was carried out by combining this model with the PI3K/AKT pathway inhibitor miltefosine to elucidate its effects on tumor proliferation. In vitro functional analysis of miR-101-3p revealed that treatment of HCC cells with its corresponding mimic significantly inhibited cell proliferation, colony formation, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Additionally, miR-101-3p exerts its anti-tumor effects by targeting the shared gene Birc5. Experiments using nude mouse models demonstrate that Birc5 promotes tumor proliferation by phosphorylating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Inhibiting the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway shows suppressive effects on liver cancer proliferation. MiR-101-3p plays crucial roles in inhibiting the proliferation, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of HCC cells by targeting Birc5 and downregulating the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway. These findings provide new insights for the molecular treatment of HCC.
Keywords: Birc5; Epithelial–mesenchymal transition; Invasion; Metastasis; MiR-101-3p.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interests: The authors of this manuscript have no conflict of interest. Ethical approval and consent to participate: The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of Shandong Provincial Hospital (approval no. SWYX:NO.2022–477). All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed in this study. Consent for publication: Not applicable.
Figures
References
-
- Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I, et al. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. Int J Cancer. 2019;144(8):1941–53. - PubMed
-
- He J, Gu D, Wu X, et al. Major causes of death among men and women in China. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(11):1124–34. - PubMed
-
- Onoue T, Uchida D, Begum NM, Tomizuka Y, Yoshida H, Sato M. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition induced by the stromal cell-derived factor-1/CXCR4 system in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol. 2006;29(5):1133–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

