Enhanced prediction of thrombotic events in hospitalized COVID-19 patients with soluble thrombomodulin
- PMID: 40106444
- PMCID: PMC11922281
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0319666
Enhanced prediction of thrombotic events in hospitalized COVID-19 patients with soluble thrombomodulin
Abstract
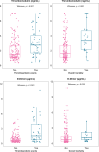
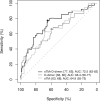
We aimed to determine the predictive accuracy of elevated soluble thrombomodulin (sTM) and angiopoietin-2 (Ang2) for thrombotic events (TE) in hospitalized COVID-19 patients. We conducted a nested case-control study within a cohort of people admitted to hospital with COVID-19 from March 2020 to August 2022. The cases (people with TE within 28 days after hospital admission) were matched by propensity score to comparable patients without TE. We determined plasma levels of sTM and Ang2 in all available frozen samples, prioritizing the earliest post-admission samples, using an automated immunoassay technique. Among 2,524 hospitalized COVID-19 patients (43% females; median age 67 years), 73 had TE (incidence 1.15 events per 1000 patient-days of follow-up). Frozen plasma samples were available for 43 cases and 176 controls. Elevated plasma concentration of sTM was significantly associated with TE (2.8 [1.8, 4] vs. 1.52 [1.1, 2.65] ng/mL; p = 0.001) and mortality (median [Q1, Q3], 3.32 [2.16, 4.65] vs. 1.58 [1.11, 2.73] ng/mL; p = 0.001), while D-dimer showed a specific association with TE (2.3 [0.8, 7.4] vs. 0.75 [0.4, 1.6] mcg/mL; p = 0.001). In contrast, Ang2 was not associated with any of these events. The association with thrombotic events remained in adjusted models (HR [95%CI] per unit increase, 1.24 [1.04-1.47] for sTM; 1.07 [1.03-1.10] for D-dimer). The adjusted regression model that included both biomarkers, sTM and D-dimer, improved (AUC 73%, sensitivity 77% and specificity 65% for TE diagnosis; p = 0.007) the predictive capacity of the same model without sTM. In conclusion, determination of soluble thrombomodulin along with D-dimer enhances thrombotic risk assessment in hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
Copyright: © 2025 Padilla et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The role of soluble thrombomodulin in the risk stratification and prognosis evaluation of septic patients in the emergency department.Thromb Res. 2013 Oct;132(4):471-6. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2013.08.011. Epub 2013 Aug 28. Thromb Res. 2013. PMID: 24035044
-
Validation of an admission coagulation panel for risk stratification of COVID-19 patients.PLoS One. 2021 Mar 19;16(3):e0248230. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248230. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33740793 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and Outcomes of D-Dimer Elevation in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020 Oct;40(10):2539-2547. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.314872. Epub 2020 Aug 25. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020. PMID: 32840379 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) infection and thrombotic conditions: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Clin Invest. 2021 Jun;51(6):e13559. doi: 10.1111/eci.13559. Epub 2021 Apr 14. Eur J Clin Invest. 2021. PMID: 33772772 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers of endothelial dysfunction and outcomes in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Microvasc Res. 2021 Nov;138:104224. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2021.104224. Epub 2021 Jul 15. Microvasc Res. 2021. PMID: 34273359 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Immunothrombosis in Sepsis: Cellular Crosstalk, Molecular Triggers, and Therapeutic Opportunities-A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 25;26(13):6114. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136114. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40649892 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

