A limitation lifted: A conditional knockdown system reveals essential roles for Polo-like kinase and Aurora kinase 1 in Trypanosoma cruzi cell division
- PMID: 40106484
- PMCID: PMC11874021
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2416009122
A limitation lifted: A conditional knockdown system reveals essential roles for Polo-like kinase and Aurora kinase 1 in Trypanosoma cruzi cell division
Abstract
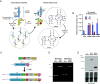
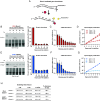
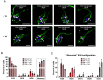
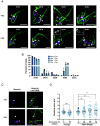
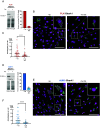
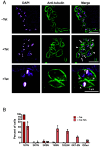
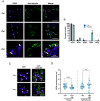
While advances in genome editing technologies have simplified gene disruption in many organisms, the study of essential genes requires development of conditional disruption or knockdown systems that are not available in most organisms. Such is the case for Trypanosoma cruzi, a parasite that causes Chagas disease, a severely neglected tropical disease endemic to Latin America that is often fatal. Our knowledge of the identity of essential genes and their functions in T. cruzi has been severely constrained by historical challenges in very basic genetic manipulation and the absence of RNA interference machinery. Here, we describe the development and use of self-cleaving RNA sequences to conditionally regulate essential gene expression in T. cruzi. Using these tools, we identified essential roles for Polo-like and Aurora kinases in T. cruzi cell division, mirroring their functions in Trypanosoma brucei. Importantly, we demonstrate conditional knockdown of essential genes in intracellular amastigotes, the disease-causing stage of the parasite in its human host. This conditional knockdown system enables the efficient and scalable functional characterization of essential genes in T. cruzi and provides a framework for the development of conditional gene knockdown systems for other nonmodel organisms.
Keywords: Trypanosoma cruzi; aptazyme; conditional knockdown; parasite; protozoan.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Functional Characterization of TcMyoF Implicates a Family of Cytostome-Cytopharynx Targeted Myosins as Integral to the Endocytic Machinery of Trypanosoma cruzi.mSphere. 2020 Jun 17;5(3):e00313-20. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00313-20. mSphere. 2020. PMID: 32554712 Free PMC article.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Field evidence of Trypanosoma cruzi infection, diverse host use and invasion of human dwellings by the Chagas disease vector in Florida, USA.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2025 Jul 7;19(7):e0012920. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012920. eCollection 2025 Jul. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2025. PMID: 40623053 Free PMC article.
-
Course of Chronic Trypanosoma cruzi Infection after Treatment Based on Parasitological and Serological Tests: A Systematic Review of Follow-Up Studies.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 5;10(10):e0139363. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0139363. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26436678 Free PMC article.
-
Over Six Thousand Trypanosoma cruzi Strains Classified into Discrete Typing Units (DTUs): Attempt at an Inventory.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016 Aug 29;10(8):e0004792. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004792. eCollection 2016 Aug. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016. PMID: 27571035 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Stable colonization of the kissing bug Rhodnius prolixus by Trypanosoma cruzi Y strain.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2025 Mar 12;19(3):e0012906. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012906. eCollection 2025 Mar. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2025. PMID: 40073048 Free PMC article.
-
Lysosome and plasma membrane Piezo channels of Trypanosoma cruzi are essential for proliferation, differentiation and infectivity.PLoS Pathog. 2025 Apr 23;21(4):e1013105. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1013105. eCollection 2025 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2025. PMID: 40267157 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Factsheet: Chagas disease in the Americas for public health workers - PAHO/WHO|Pan American Health Organization, https://www.paho.org/en/documents/factsheet-chagas-disease-americas-publ.... 27 January 2022. cited 22 May 2024.
-
- Brener Z., Life cycle of Trypanosoma cruzi. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 13, 171–178 (1971). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

