Differential gene expression patterns in Niemann-Pick Type C and Tay-Sachs diseases: Implications for neurodegenerative mechanisms
- PMID: 40106490
- PMCID: PMC11922228
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0319401
Differential gene expression patterns in Niemann-Pick Type C and Tay-Sachs diseases: Implications for neurodegenerative mechanisms
Abstract
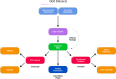
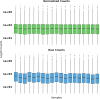
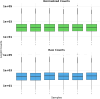
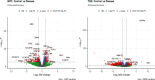
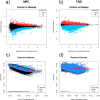
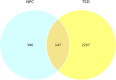
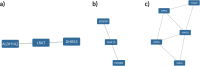
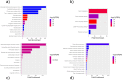
Lysosomal storage disorders (LSDs) are a group of rare genetic conditions characterized by the impaired function of enzymes responsible for lipid digestion. Among these LSDs, Tay-Sachs disease (TSD) and Niemann-Pick type C (NPC) may share a common gene expression profile. In this study, we conducted a bioinformatics analysis to explore the gene expression profile overlap between TSD and NPC. Analyses were performed on RNA-seq datasets for both TSD and NPC from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. Datasets were subjected to differential gene expression analysis utilizing the DESeq2 package in the R programming language. A total of 147 differentially expressed genes (DEG) were found to be shared between the TSD and NPC datasets. Enrichment analysis was then performed on the DEGs. We found that the common DEGs are predominantly associated with processes such as cell adhesion mediated by integrin, cell-substrate adhesion, and urogenital system development. Furthermore, construction of protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks using the Cytoscape software led to the identification of four hub genes: APOE, CD44, SNCA, and ITGB5. Those hub genes not only can unravel the pathogenesis of related neurologic diseases with common impaired pathways, but also may pave the way towards targeted gene therapy of LSDs.In addition, they serve as the potential biomarkers for related neurodegenerative diseases warranting further investigations.
Copyright: © 2025 Yousefpour Shahrivar et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Progranulin associates with hexosaminidase A and ameliorates GM2 ganglioside accumulation and lysosomal storage in Tay-Sachs disease.J Mol Med (Berl). 2018 Dec;96(12):1359-1373. doi: 10.1007/s00109-018-1703-0. Epub 2018 Oct 20. J Mol Med (Berl). 2018. PMID: 30341570 Free PMC article.
-
Finding pathogenic commonalities between Niemann-Pick type C and other lysosomal storage disorders: Opportunities for shared therapeutic interventions.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020 Oct 1;1866(10):165875. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2020.165875. Epub 2020 Jun 6. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020. PMID: 32522631 Review.
-
A master protocol to investigate a novel therapy acetyl-L-leucine for three ultra-rare neurodegenerative diseases: Niemann-Pick type C, the GM2 gangliosidoses, and ataxia telangiectasia.Trials. 2021 Jan 22;22(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-05009-3. Trials. 2021. PMID: 33482890 Free PMC article.
-
Neural stem cells for disease modeling and evaluation of therapeutics for Tay-Sachs disease.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2018 Sep 17;13(1):152. doi: 10.1186/s13023-018-0886-3. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2018. PMID: 30220252 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring nasopharyngeal carcinoma genetics: Bioinformatics insights into pathways and gene associations.Med J Malaysia. 2024 Sep;79(5):615-625. Med J Malaysia. 2024. PMID: 39352166 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in Diagnosis, Pathological Mechanisms, Clinical Impact, and Future Therapeutic Perspectives in Tay-Sachs Disease.Neurol Int. 2025 Jun 25;17(7):98. doi: 10.3390/neurolint17070098. Neurol Int. 2025. PMID: 40710901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-4537 curtails ferroptosis by targeting MIOX in renal cell carcinoma.Transl Oncol. 2025 Jun;56:102401. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2025.102401. Epub 2025 Apr 29. Transl Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40306150 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

