Insights into Octopus maya cathepsins from metatranscriptome and genome: structure evolutionary relationships and functional role prediction in digestive processes
- PMID: 40106538
- PMCID: PMC12032550
- DOI: 10.1242/bio.061778
Insights into Octopus maya cathepsins from metatranscriptome and genome: structure evolutionary relationships and functional role prediction in digestive processes
Abstract
Physiological response to feeding is crucial for various production factors such as feed catabolism and growth. Despite growing significance in red Octopus maya aquaculture, large-scale commercial production is limited by not sufficiently knowing their nutritional needs, especially their digestive physiology. Since this species is carnivorous, one of the main feeding aspects is directed to protein digestion, but its enzymatic digestive repertoire has not been studied yet at genomic and transcriptomic levels. This study searched for protease enzymes encoded in O. maya genome and expressed in the transcriptome, allowing an initial annotation of genes involved in protein catabolism; 117 amino acid sequences related to 'octopus digestive enzymes' were retrieved from 66 available-species' genomes in the NCBI database, coding for cathepsins, papilins, and metalloproteases. Homology analysis identified 36 homologous sequences from O. maya transcriptome and three from its genome. Phylogenetic analysis grouped 37 of 39 sequences into 11 of 14 main clades, offering new insights into the evolutionary relationships and functional roles of these proteases. Phylogenetic and motif analyses resulted in selecting 19 amino acid O. maya sequences using multiple sequence alignment that were used to generate three-dimensional protein models. The obtained models revealed a diverse structural architecture among 16 modelled cathepsins; however, their catalytic potential to fully clarify their role in protein hydrolysis and cellular processes remains to be determined. Foundational data provides insights into biochemistry and physiology behind O. maya protein digestion. Further complementation of these results with enzymatic characterization of the identified proteases should allow for improved diet formulation in order to foster this species aquaculture.
Keywords: Octopus maya; Cathepsin; Digestive physiology; Genome; Metatranscriptome.
© 2025. Published by The Company of Biologists.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures
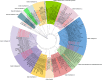


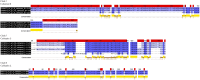

Similar articles
-
Evaluation of Octopus maya enzyme activity of the digestive gland and gastric juice.Biol Open. 2024 Sep 15;13(9):bio060429. doi: 10.1242/bio.060429. Epub 2024 Sep 12. Biol Open. 2024. PMID: 39140156 Free PMC article.
-
Digestive Physiology of Octopus maya and O. mimus: Temporality of Digestion and Assimilation Processes.Front Physiol. 2017 May 31;8:355. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00355. eCollection 2017. Front Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28620313 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biochemical, transcriptomic and proteomic analyses of digestion in the scorpion Tityus serrulatus: insights into function and evolution of digestion in an ancient arthropod.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 15;10(4):e0123841. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0123841. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25875018 Free PMC article.
-
Recruitment of lysosomal cathepsins B, L and D as digestive enzymes in Coleoptera.Insect Mol Biol. 2022 Apr;31(2):225-240. doi: 10.1111/imb.12753. Epub 2021 Dec 28. Insect Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34918424
-
Insight into crustacean cathepsins: Structure-evolutionary relationships and functional roles in physiological processes.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023 Aug;139:108852. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2023.108852. Epub 2023 Jun 7. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37295735 Review.
Cited by
-
Polystyrene Microplastic Interferes with Yolk Reserve Utilisation in Early Artemia salina Nauplii.Toxics. 2025 Aug 20;13(8):700. doi: 10.3390/toxics13080700. Toxics. 2025. PMID: 40863975 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agarwal, S. K., Singh, S. and Sharma, S. (2020). Structural and functional dynamics of lysosomal cysteine proteases with particular reference to Cathepsin B and Cathepsin H. In Frontiers in Protein Structure, Function, and Dynamics (ed. Singh D. and Tripathi T.), pp. 391-424. Singapore: Springer Singapore. 10.1007/978-981-15-5530-5_16 - DOI
-
- Aguila, J., Cuzon, G., Pascual, C., Domingues, P. M., Gaxiola, G., Sánchez, A., Maldonado, T. and Rosas, C. (2007). The effects of fish hydrolysate (CPSP) level on Octopus maya (Voss and Solis) diet: digestive enzyme activity, blood metabolites, and energy balance. Aquaculture 273, 641-655. 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2007.07.010 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

