A plant peptide with dual activity against multidrug-resistant bacterial and fungal pathogens
- PMID: 40106560
- PMCID: PMC11922054
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adt8239
A plant peptide with dual activity against multidrug-resistant bacterial and fungal pathogens
Abstract
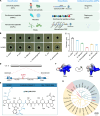
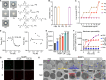
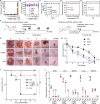
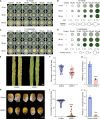
Multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria pose a major threat to public health, and additional sources of antibacterial candidates are urgently needed. Noncanonical peptides (NCPs), derived from noncanonical small open reading frames, represent small biological molecules with important roles in biology. However, the antibacterial activity of NCPs remains largely unknown. Here, we discovered a plant-derived noncanonical antibacterial peptide (NCBP1) against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. NCBP1 is composed of 11 amino acid residues with cationic surface potential and favorable safety and stability. Mechanistic studies revealed that NCBP1 displayed antibacterial activity by targeting phosphatidylglycerol and cardiolipin in bacterial membrane, resulting in membrane damage and dysfunction. Notably, NCBP1 showed promising efficacy in mice. Furthermore, NCBP1 effectively inhibited the growth of plant fungal pathogens and enhanced disease resistance in maize. Our results demonstrate the unexplored antimicrobial potential of plant-derived NCPs and provide an accessible source for the discovery of antimicrobial substances against MDR bacterial and fungal pathogens.
Figures


References
-
- Gollan B., Grabe G., Michaux C., Helaine S., Bacterial persisters and infection: Past, present, and progressing. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 73, 359–385 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Lewis K., The science of antibiotic discovery. Cell 181, 29–45 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Laxminarayan R., Sridhar D., Blaser M., Wang M. G., Woolhouse M., Achieving global targets for antimicrobial resistance. Science 353, 874–875 (2016). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

