Operant effort-based decision-making task reveals sex differences in motivational behavior but no long-term effects of adolescent intermittent ethanol in Sprague Dawley rats
- PMID: 40107424
- PMCID: PMC12365859
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pbb.2025.173998
Operant effort-based decision-making task reveals sex differences in motivational behavior but no long-term effects of adolescent intermittent ethanol in Sprague Dawley rats
Abstract
Loss of motivated behavior, or apathy, is a key feature across multiple affective disorders, and is assessed via operant effort-based decision-making (EBDM). The mechanisms of amotivation have been connected to pro-inflammatory signaling which can directly impact dopamine signaling. Chronic alcohol exposure is associated with altered immune signaling and impaired goal-directed behavior, so the present studies assessed the impact of adolescent intermittent ethanol (AIE) on EBDM in adulthood across sex. Adolescent male and female (N = 32/n = 8 per group) Sprague-Dawley rats were exposed to ethanol (4 g/kg) intragastrically on a 3 days on/2 days off schedule during postnatal days ~30-50 or given vehicle, and allowed to age into adulthood (P80+). All rats were then trained on the operant EBDM concurrent FR5/chow task, after which we tested the impact of sex and AIE history on responding 1) during breakpoint challenge raising the FR requirement in a log2 pattern, 2) 90 min after immune challenge (2 μg/kg IL-1β), 3) 18 h after 3.5 g/kg intraperitoneal ethanol challenge (hangover), and 4) immediately after a 30-min restraint stress challenge. Immune challenge disrupted motivated behavior without affecting appetite. No effects of AIE emerged and sex differences were evident throughout all challenges. Females responded less for pellets yet persisted responding until a higher breakpoint. This work indicates that AIE does not alter baseline or evoked EBDM as can be measured with this approach. Testing across aging and using other modalities should be performed to continue examining the effects of chronic alcohol on apathy.
Keywords: Adolescent intermittent ethanol; Effort-based decision making; Hangover; IL-1; Sex differences; Stress.
Copyright © 2025 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures





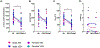
Similar articles
-
Adolescent intermittent ethanol (AIE) sensitized fever in male Sprague Dawley rats exposed to poly I:C in adulthood.Brain Behav Immun. 2024 Aug;120:82-97. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2024.05.027. Epub 2024 May 21. Brain Behav Immun. 2024. PMID: 38777284 Free PMC article.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Sex differences in the social motivation of rats: Insights from social operant conditioning, behavioural economics, and video tracking.Biol Sex Differ. 2024 Jul 19;15(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s13293-024-00612-4. Biol Sex Differ. 2024. PMID: 39030614 Free PMC article.
-
NTP Developmental and Reproductive Toxicity Technical Report on the Prenatal Development Studies of 2-((1-(4-Phenoxyphenoxy)propan-2-yl)oxy)pyridine (CASRN 95737-68-1) in Sprague Dawley (Hsd:Sprague Dawley® SD®) Rats and New Zealand White (Hra:NZW SPF) Rabbits: DART Report 07 [Internet].Research Triangle Park (NC): National Toxicology Program; 2022 Jan. Research Triangle Park (NC): National Toxicology Program; 2022 Jan. PMID: 35593777 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

