Cardioprotective effects of semaglutide on isolated human ventricular myocardium
- PMID: 40107718
- PMCID: PMC12370581
- DOI: 10.1002/ejhf.3644
Cardioprotective effects of semaglutide on isolated human ventricular myocardium
Abstract
Aims: Semaglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, has shown promising effects in reducing cardiovascular events in patients with obesity and heart failure (HF) with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) irrespective of concomitant diabetes. However, the exact mechanisms underlying its cardioprotective actions remain unclear. Our study investigates the direct effects of semaglutide on human cardiomyocytes, focusing on calcium (Ca) and sodium (Na) handling and its potential to improve myocardial contractility.
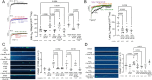
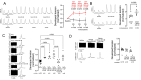
Methods and results: Human left ventricular cardiomyocytes were isolated from non-failing (NF) hearts, patients with aortic stenosis and a HFpEF-like phenotype (AS), and those with end-stage HF with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). Late Na current (INa), sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) Ca leak, and contractility were assessed in isolated cardiomyocytes treated with semaglutide. CaMKII inhibitor autocamtide-2-related inhibitory peptide and GLP-1 receptor antagonist exendin 9-39 (Ex-9-39) were used to elucidate signalling pathways. Semaglutide reduced late INa in AS and HFrEF cardiomyocytes to levels comparable to NF. Additionally, semaglutide decreased diastolic SR Ca leak and improved systolic Ca transients and contractility in AS and HFrEF tissue. These effects were mediated through GLP-1 receptor agonism and were comparable to CaMKII inhibition. In multicellular preparations, semaglutide differentially improved myocardial contractility in AS and HFrEF in a dose-dependent manner.
Conclusion: Semaglutide directly modulates ion homeostasis in human cardiomyocytes, reducing proarrhythmic diastolic SR Ca leak and enhancing systolic function, which may explain its observed clinical benefits. These findings provide mechanistic insights into the cardioprotective effects of semaglutide and suggest its potential therapeutic use in HF.
Keywords: Calcium; Heart failure; Human cardiomyocytes; Semaglutide.
© 2025 The Author(s). European Journal of Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Society of Cardiology.
Figures

References
-
- Deanfield J, Verma S, Scirica BM, Kahn SE, Emerson SS, Ryan D, et al.; SELECT Trial Investigators . Semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with obesity and prevalent heart failure: A prespecified analysis of the SELECT trial. Lancet 2024;404:773–786. 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)01498-3 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

