Azoramide, a novel regulator, favors adipogenesis against osteogenesis through inhibiting the GLP-1 receptor-PKA-β-catenin pathway
- PMID: 40108027
- PMCID: PMC11923014
- DOI: 10.1007/s13577-025-01192-0
Azoramide, a novel regulator, favors adipogenesis against osteogenesis through inhibiting the GLP-1 receptor-PKA-β-catenin pathway
Abstract
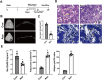
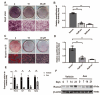
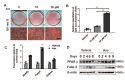
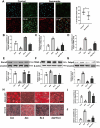
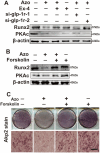
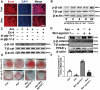
The reciprocal fate decision of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) to either bone or adipocytes is determined by Wnt-related signaling and the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R). Azoramide, an ER stress alleviator, was reported to have an antidiabetic effect. In this study, we investigated the function of azoramide in regulating the lineage determination of MSCs for either adipogenic or osteogenic differentiation. Microcomputed tomography and histological analysis on bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)2-induced parietal periosteum bone formation assays, C3H10T1/2 and mouse bone marrow MSC-derived bone formation and adipogenesis assays, and specific staining for bone tissue and lipid droplets were used to evaluate the role of azoramide on the lineage determination of MSC differentiation. Cells were harvested for Western blot and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR), and immunofluorescence staining was used to explore the potential mechanism of azoramide for regulating MSC differentiation. Based on MSC-derived bone formation assays both in vivo and in vitro, azoramide treatment displayed a cell fate determining ability in favor of adipogenesis over osteogenesis. Further mechanistic characterizations disclosed that both the GLP-1R agonist peptide exendin-4 (Ex-4) and GLP-1R small interfering (si)RNA abrogated azoramide dual effects. Moreover, cAMP-protein kinase A (PKA)-mediated nuclear β-catenin activity was responsible for the negative function of azoramide on bone formation in favor of adipogenesis. These data provide the first evidence to show that azoramide may serve as an inhibitor against GLP-1R in MSC lineage determination.
Keywords: Adipogenesis; Azoramide; Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor; MSC; Osteogenesis; Wnt.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval: This study was carried out in accordance with the recommendations in the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the National Institutes of Health. All animal care and experimental procedures were performed under approval of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Fourth Military Medical University (approval no. KY20150042-1). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Azoramide, a novel regulator, favors adipogenesis against osteogenesis through inhibiting the GLP-1 receptor-PKA-β-catenin pathway.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018 Mar 9;9(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s13287-018-0771-y. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018. Retraction in: Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023 Sep 29;14(1):275. doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03513-2. PMID: 29523188 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Icariin stimulates osteogenesis and suppresses adipogenesis of human bone mesenchymal stem cells via miR-23a-mediated activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Phytomedicine. 2021 May;85:153485. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153485. Epub 2021 Jan 29. Phytomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33743412
-
Liraglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, facilitates osteogenic proliferation and differentiation in MC3T3-E1 cells through phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT), extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK)1/2, and cAMP/protein kinase A (PKA) signaling pathways involving β-catenin.Exp Cell Res. 2017 Nov 15;360(2):281-291. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.09.018. Epub 2017 Sep 15. Exp Cell Res. 2017. PMID: 28919123
-
PPARγ and Wnt Signaling in Adipogenic and Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;11(3):216-25. doi: 10.2174/1574888x10666150519093429. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 25986621 Review.
-
Molecular switching of osteoblastogenesis versus adipogenesis: implications for targeted therapies.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2009 May;13(5):593-603. doi: 10.1517/14728220902915310. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2009. PMID: 19397478 Review.
References
-
- Yan Z, Ruan B, Wang S, Du T, Shao X, Chen G, et al. RNA-binding protein QKI inhibits osteogenic differentiation via suppressing Wnt pathway. Arch Med Res. 2023;54(5): 102853. - PubMed
-
- Ross SE, Hemati N, Longo KA, Bennett CN, Lucas PC, Erickson RL, et al. Inhibition of adipogenesis by Wnt signaling. Science (New York NY). 2000;289(5481):950–3. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

