Comprehensive machine learning assessment of zebrafish behaviour and biochemical markers in response to caffeine exposure
- PMID: 40108086
- PMCID: PMC12254161
- DOI: 10.1007/s10646-025-02873-0
Comprehensive machine learning assessment of zebrafish behaviour and biochemical markers in response to caffeine exposure
Abstract
Environmental exposure to caffeine (CAF) poses potential risks to aquatic ecosystems, affecting non-target species. This study investigated the chronic effects of environmentally relevant CAF concentrations, ranging from 0.16-50 µg/L, on zebrafish behaviour. A Kohonen-type artificial neural network classified zebrafish behaviour into nine behavioural classes based on a set of movement descriptors (mean meander, mean velocity, instantaneous velocity, distance to centre point, mean angular velocity and instantaneous acceleration), while a comprehensive analysis integrated behavioural classes previously defined and biochemical markers of oxidative stress, lipid peroxidation, reserve energy content, energetic pathways, and neurotoxicity. The discriminant analysis demonstrated that behaviour descriptors and biomarkers individually explained 38% and 67% of data variation, respectively, while the combination resulted in 19 models with 100% correct diagnosis. One of the models (Model A) seemed to suit the best dose-response relationship, incorporating key biomarkers including superoxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione peroxidase activities, and behavioural characteristics such as movement distance and velocity. This suggested methodology offers a different approach to evaluating CAF's ecological impact, highlighting behavioural analysis as a valuable complement to traditional ecotoxicological assessments. This study provides a novel framework for understanding organism-level responses to environmental stressors (e.g., several anthropogenic compounds), utilising Mahalanobis distance as an integrative response index. This approach shows promise for broader application in assessing the impact of various aquatic contaminants on aquatic organisms (from bacteria to fish), potentially extending to pharmaceuticals, pesticides, and industrial pollutants.
Keywords: Danio rerio; Biochemical markers; Ecotoxicology; Integrated assessment; Locomotor behaviour; Mahalanobis distance.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with ethical standards. Conflict of interest: The author declares no competing interests.
Figures


 highest distance to the centre;
highest distance to the centre;  highest mean velocity and mean angular velocity;
highest mean velocity and mean angular velocity;  low distance to the centre
low distance to the centre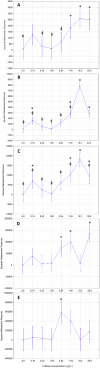
Similar articles
-
Environmental caffeine triggers oxidative stress and behavioral changes in Cyprinus carpio: Insights into neurotoxicity.Behav Brain Res. 2025 Sep 13;493:115695. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2025.115695. Epub 2025 Jun 7. Behav Brain Res. 2025. PMID: 40490105
-
A comprehensive review on the neurobehavioural effects of bisphenol compounds and the underlying molecular mechanisms in zebrafish (Danio rerio).Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2025 Oct;296:110228. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpc.2025.110228. Epub 2025 May 18. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40393573 Review.
-
Ecotoxicological assessment of pesticide mixtures: effects of imidacloprid and propiconazole on Danio rerio and Astyanax lacustris.Aquat Toxicol. 2025 Oct;287:107544. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2025.107544. Epub 2025 Aug 16. Aquat Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40840309
-
Transcriptomic and microbiota responses in Mytilus galloprovincialis exposed to environmental concentrations of caffeine and cocaine.Aquat Toxicol. 2025 Sep;286:107458. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2025.107458. Epub 2025 Jun 13. Aquat Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40543326
-
Psychological interventions for adults who have sexually offended or are at risk of offending.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Dec 12;12(12):CD007507. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007507.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 23235646 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Impact of Caffeine on Aquatic Ecosystems: Assessing Trophic-Level Biological Responses.J Xenobiot. 2025 Jun 3;15(3):86. doi: 10.3390/jox15030086. J Xenobiot. 2025. PMID: 40558869 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abreu IO, Monteiro C, Rocha ACS, Reis-Henriques MA, Teixeira C, Basto MCP, Ferreira M, Almeida CMR, Oliva-Teles L, Guimarães L (2018) Multibiomarker interactions to diagnose and follow-up chronic exposure of a marine crustacean to hazardous and noxious substances (HNS). Environ Pollut 242:1137–1145. 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.07.106 - PubMed
-
- Amorim J, Fernandes M, Vasconcelos V, Oliva Teles L (2017) Evaluation of the sensitivity spectrum of a video tracking system with zebrafish (Danio rerio) exposed to five different toxicants. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24:16086–16096. 10.1007/s11356-017-9262-4 - PubMed
-
- Amorim J, Fernandes M, Abreu I, Tavares F, Oliva-Teles L (2018) Escherichia coli’s water load affects zebrafish (Danio rerio) behaviour. Sci Total Environ 636:767–774. 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.316 - PubMed
-
- Andrade TS, Henriques JF, Almeida AR, Machado AL, Koba O, Giang PT, Soares AMVM, Domingues I (2016) Carbendazim exposure induces developmental biochemical and behavioural disturbance in zebrafish embryos. Aquat Toxicol 170:390–399. 10.1016/j.aquatox.2015.11.017 - PubMed
-
- Angelucci MEM, Cesário C, Hiroi RH, Rosalen PI, da Cunha C (2002) Effects of caffeine on learning and memory in rats tested in the morris water maze. Braz J Med Biol Res 35:1201–1208. 10.1590/s0100-879x2002001000013 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2022.10117.BD/Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia
- doi: 10.54499/2020.00464.CEECIND/CP1599/CT0002/Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia
- SFRH/BD/135681/2018/Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia
- 2022.10505.BD/Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia
- 2022.10194.BD/Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

