Association between the indicators of insulin resistance and periodontitis: a study using data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2009-2014
- PMID: 40108596
- PMCID: PMC11924845
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-025-05752-6
Association between the indicators of insulin resistance and periodontitis: a study using data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2009-2014
Abstract
Background: The rising obesity rates are accompanied by an increasing prevalence of insulin resistance (IR) associated with obesity. To ascertain the best index for replacing IR, this study aimed to investigate the possible association between IR, which was assessed using the Homeostatic Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR), and the triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index and its derived indexes and periodontitis.
Methods: The association between the indicators of IR and periodontitis was assessed via multivariate-adjusted logistic regression analyses using data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2009-2014. In addition, subgroup analyses and receiver operating characteristic curve analyses were conducted to explore possible influencing factors.
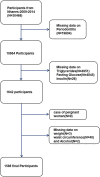
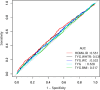
Results: Our study encompassed 1,588 participants, and 41.0% were diagnosed with periodontitis. Based on the multivariate logistic regression analysis, a higher TyG-waist-to-height ratio (WHtR) (odds ratio [OR] = 1.14, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.02-1.27, P = 0.0244) and HOMA-IR score (OR = 1.00, 95% CI: 1.00-1.00, P = 0.0028) were associated with an increased risk of periodontitis. Conversely, the TyG index, TyG-adjusted for body mass index, and TyG-adjusted for waist circumference (WC) were not associated with periodontitis. According to further subgroup analyses and interaction result analyses, sex affected the association between the TyG index, TyG-WC, and TyG-WHtR and periodontitis (P < 0.05 for interaction). Moreover, the influence of age regulated the association between periodontitis and both TyG and HOMA-IR score. In terms of diagnostic accuracy, the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve analysis revealed that HOMA-IR score and TyG-WHtR slightly outperformed the TyG index, TyG-body mass index, and TyG-WC. Thus, they can be robust markers for assessing IR-related periodontitis risk.
Conclusion: A consistent and positive association was found between HOMA-IR score and TyG-WHtR and the odds of periodontitis prevalence. Hence, HOMA-IR score and TyG-WHtR were significantly associated with periodontitis in this cross-sectional study. However, prospective studies are needed to determine whether higher TyG-waist-to-height ratio and HOMA-IR score can predict the occurrence of periodontitis.
Keywords: A cross-sectional study; NHANES; Periodontitis; Relationship; TyG-related indicators.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was conducted by the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the National Centre for Health Statistics. All participants provided informed consent before enrollment. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Potential of seven insulin resistance indicators as biomarkers to predict infertility risk in U.S. women of reproductive age: a cross-sectional study.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2025 May 24;23(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s12958-025-01416-w. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2025. PMID: 40413481 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between different triglyceride glucose index-related obesity indices and periodontitis: results from NHANES 2009-2014.Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Jul 5;23(1):213. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02192-z. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 38970059 Free PMC article.
-
Association between triglyceride glucose-waist to height ratio (TyG-WHtR) and hypertension in adults aged 18-60: a cross-sectional study.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025 May 26;25(1):403. doi: 10.1186/s12872-025-04853-y. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025. PMID: 40419977 Free PMC article.
-
Association between triglyceride glucose index-related indices and kidney stones in adults based on NHANES 2007-2020.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Jan 7;15:1516982. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1516982. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 39839481 Free PMC article.
-
Association of triglyceride glucose and obesity indices with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in US adults: data from 2013 to 2018 NHANES.BMC Pulm Med. 2025 May 28;25(1):268. doi: 10.1186/s12890-025-03738-2. BMC Pulm Med. 2025. PMID: 40437398 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Association of overactive bladder with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in women: A propensity-matched NHANES study.BJUI Compass. 2025 Apr 29;6(5):e70022. doi: 10.1002/bco2.70022. eCollection 2025 May. BJUI Compass. 2025. PMID: 40313594 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arboleda S, Vargas M, Losada S, Pinto A. Review of obesity and periodontitis: an epidemiological view. Br Dent J. 2019;227(3):235–9. 10.1038/s41415-019-0611-1. - PubMed
-
- Ashwell M, Gunn P, Gibson S. Waist-to-height ratio is a better screening tool than waist circumference and BMI for adult cardiometabolic risk factors: systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Rev. 2012;13(3):275–86. 10.1111/j.1467-789X.2011.00952.x. - PubMed
-
- Blasco-Baque V, Garidou L, Pomié C, Escoula Q, Loubieres P, Le Gall-David S, Lemaitre M, Nicolas S, Klopp P, Waget A, Azalbert V, Colom A, Bonnaure-Mallet M, Kemoun P, Serino M, Burcelin R. Periodontitis induced by Porphyromonas gingivalis drives periodontal microbiota dysbiosis and insulin resistance via an impaired adaptive immune response. Gut. 2017;66(5):872–85. 10.1136/gutjnl-2015-309897. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Borgnakke, W. S., Genco, R. J., Eke, P. I., & Taylor, G. W. (2018). Oral Health and Diabetes. In C. C. Cowie et al. (Eds.), Diabetes in America (3rd ed., pp. 24-1–24-20). National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (US). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK567979/. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources