Enhancing diagnostics: ChatGPT-4 performance in ulcerative colitis endoscopic assessment
- PMID: 40109324
- PMCID: PMC11922305
- DOI: 10.1055/a-2542-0943
Enhancing diagnostics: ChatGPT-4 performance in ulcerative colitis endoscopic assessment
Abstract
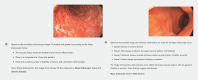
Background and study aims: The Mayo Endoscopic Subscore (MES) is widely utilized for assessing mucosal activity in ulcerative colitis (UC). Artificial intelligence has emerged as a promising tool for enhancing diagnostic precision and addressing interobserver variability. This study evaluated the diagnostic accuracy of ChatGPT-4, a multimodal large language model, in identifying and grading endoscopic images of UC patients using the MES.
Patients and methods: Real-world endoscopic images of UC patients were reviewed by an expert consensus board. Each image was graded based on the MES. Only images that were uniformly graded were subsequently provided to three inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) specialists and ChatGPT-4. Severity gradings of the IBD specialists and ChatGPT-4 were compared with assessments made by the expert consensus board.
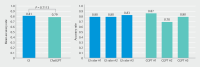
Results: Thirty of 50 images were graded with complete agreement among the experts. Compared with the consensus board, ChatGPT-4 gradings had a mean accuracy rate of 78.9% whereas the mean accuracy rate for the IBD specialists was 81.1%. Between the two groups, there was no statistically significant difference in mean accuracy rates ( P = 0.71) and a high degree of reliability was found.
Conclusions: ChatGPT-4 has the potential to assess mucosal inflammation severity from endoscopic images of UC patients, without prior configuration or fine-tuning. Performance rates were comparable to those of IBD specialists.
Keywords: Diagnosis and imaging (inc chromoendoscopy, NBI, iSCAN, FICE, CLE...); Endoscopy Lower GI Tract; Image and data processing, documentatiton; Inflammatory bowel disease; Quality and logistical aspects.
The Author(s). This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, permitting unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction so long as the original work is properly cited. (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Application of deep learning in the diagnosis and evaluation of ulcerative colitis disease severity.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2023 Dec 22;16:17562848231215579. doi: 10.1177/17562848231215579. eCollection 2023. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 38144424 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Performance of a Fecal Calprotectin Assay as a Biomarker for Mayo Endoscopic Subscore in Ulcerative Colitis: Result From a Tertiary Referral Center.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2024 Dec 5;30(12):2347-2355. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izae005. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2024. PMID: 38309716
-
A Novel Switching of Artificial Intelligence to Generate Simultaneously Multimodal Images to Assess Inflammation and Predict Outcomes in Ulcerative Colitis-(With Video).Dig Endosc. 2025 Jun 16. doi: 10.1111/den.15067. Online ahead of print. Dig Endosc. 2025. PMID: 40518924
-
Artificial intelligence in gastrointestinal endoscopy for inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review and new horizons.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2021 Jun 10;14:17562848211017730. doi: 10.1177/17562848211017730. eCollection 2021. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 34178115 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How to assess endoscopic disease activity in ulcerative colitis in 2022.Ann Gastroenterol. 2022 Sep-Oct;35(5):462-470. doi: 10.20524/aog.2022.0732. Epub 2022 Jul 11. Ann Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36061162 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Colombel JF, Rutgeerts P, Reinisch W et al.Early mucosal healing with infliximab is associated with improved long- term clinical outcomes in ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 2011;141:1194–1201. - PubMed
-
- Turner D, Ricciuto A, Lewis A et al.STRIDE-II: An update on the Selecting Therapeutic Targets in Inflammatory Bowel Disease (STRIDE) Initiative of the International Organization for the Study of IBD (IOIBD): determining therapeutic goals for treat-to-target strategies in IBD. Gastroenterology. 2021;160:1570–1583. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.12.031. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schroeder K, Tremanie W, Ilstrup D. Coated Oral 5-aminosalicylic acid therapy for mildly to moderately active ulcerative colitis. A randomized study. N Engl J Med. 1987;317:1625–1629. - PubMed
-
- Osada T, Ohkusa T, Yokoyama T et al.Comparison of several activity indices for the evaluation of endoscopic activity in UC: Inter- and intraobserver consistency. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. 2010;16:192–197. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous