Serum metabolomic analysis identified serum biomarkers predicting tumour recurrence after Bacillus Calmette-Guérin therapy in patients with non-muscle invasive bladder cancer
- PMID: 40109498
- PMCID: PMC11921002
- DOI: 10.1177/23523735251325100
Serum metabolomic analysis identified serum biomarkers predicting tumour recurrence after Bacillus Calmette-Guérin therapy in patients with non-muscle invasive bladder cancer
Abstract
Background: Metabolomic research and metabolomics-based biomarkers predicting treatment outcomes in bladder cancer remain limited.
Objective: We explored the serum metabolites potentially associated with the risk of recurrence after intravesical Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) therapy.
Methods: Two independent cohorts, a discovery cohort (n = 23) and a validation cohort (n = 40), were included in this study. Blood was collected before the induction of BCG therapy (pre-BCG blood; both discovery and validation cohorts) and after six doses of BCG (post-BCG blood; only discovery cohort). Metabolome analysis of serum samples was conducted using capillary electrophoresis time-of-flight mass spectrometry. The endpoint was intravesical recurrence-free survival, which was analysed using Kaplan-Meier estimates, the log-rank test, and the Cox proportional hazard model.
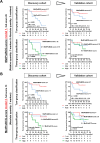
Results: Of the 353 metabolites quantified, nine (2.5%) and four (1.1%) were significantly upregulated and downregulated, respectively. The heatmap of hierarchical clustering analysis and principal coordinate analysis for the fold changes and in serum metabolites differentiated 10 recurrent cases and 13 non-recurrent cases in the discovery cohort. A metabolome response-based scoring model using 16 metabolites, including threonine and N6,N6,N6-trimethyl-lysine effectively stratified the risk of post-BCG recurrence. Additionally, pre-BCG metabolome-based score models using six metabolites, octanoylcarnitine, S-methylcysteine-S-oxide, theobromine, carnitine, indole-3-acetic acid, and valeric acid, were developed from the discovery cohort. Univariate and multivariate analyses confirmed a high predictive accuracy in the validation and combination cohorts.
Conclusions: We demonstrated that numerous types of serum metabolites were altered in response to intravesical BCG and developed high-performance score models which might effectively differentiated the risk of post-BCG tumour recurrence.
Keywords: BCG; Bacillus Calmette-Guerin; metabolites; metabolomics; mycobacterium bovis; prognosis; recurrence; serum; urinary bladder neoplasms.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A Phase 1/2 Single-arm Clinical Trial of Recombinant Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) VPM1002BC Immunotherapy in Non-muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer Recurrence After Conventional BCG Therapy: SAKK 06/14.Eur Urol Oncol. 2022 Apr;5(2):195-202. doi: 10.1016/j.euo.2021.12.006. Epub 2022 Jan 7. Eur Urol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35012889 Clinical Trial.
-
Single immediate instillation of chemotherapy is associated with decreased recurrence and progression in patients with high-risk non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer who receive adjuvant induction bacillus Calmette-Guérin therapy.Int J Urol. 2022 Aug;29(8):867-875. doi: 10.1111/iju.14926. Epub 2022 May 16. Int J Urol. 2022. PMID: 35577361
-
Elevated T-cell Exhaustion and Urinary Tumor DNA Levels Are Associated with Bacillus Calmette-Guérin Failure in Patients with Non-muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer.Eur Urol. 2022 Dec;82(6):646-656. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2022.09.008. Epub 2022 Oct 7. Eur Urol. 2022. PMID: 36210217
-
Clinical and Preclinical Therapies for Bladder Cancer Following Bacillus Calmette-Guérin Failure.J Urol. 2023 Jan;209(1):32-48. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000002957. Epub 2022 Sep 6. J Urol. 2023. PMID: 36067380
-
International Bladder Cancer Group Consensus Statement on Clinical Trial Design for Patients with Bacillus Calmette-Guérin-exposed High-risk Non-muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer.Eur Urol. 2022 Jul;82(1):34-46. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2021.12.005. Epub 2021 Dec 23. Eur Urol. 2022. PMID: 34955291 Review.
References
-
- EAU Guidelines. Edn. presented at the EAU Annual Congress Paris 2024. ISBN 978-94-92671-23-3. EAU Guidelines Office, Arnhem, The Netherlands. https://uroweb.org/guidelines.
-
- Babjuk M, Burger M, Capoun O, et al. European association of urology guidelines on non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (Ta, T1, and Carcinoma in Situ). Eur Urol 2022; 81: 75–94. - PubMed
-
- Matsumoto H, Shiraishi K, Azuma H, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for bladder cancer 2019 update by the Japanese urological association: summary of the revision. Int J Urol 2020; 27: 702–709. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

