Extensive surveillance of mosquitoes and molecular investigation of arboviruses in Central Iran
- PMID: 40109650
- PMCID: PMC11918787
- DOI: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000002826
Extensive surveillance of mosquitoes and molecular investigation of arboviruses in Central Iran
Abstract
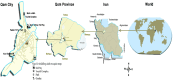
Background: Arboviruses are one of the greatest threats to animal and public health. Culicidae family is one of the most important vectors for the transmission of arboviruses in the world. According to the geographical, demographic, and climatic features of Qom city in Iran, it can be a suitable region for vectors and therefore transmission of arboviruses.
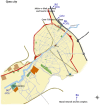
Methods: In this study, which was conducted between 2019 and 2020 in different parts of Qom city, 83 414 mosquitoes were collected, and after evaluating the species of mosquitoes based on morphological and molecular detection, the presence of alphaviruses, flaviviruses, and phleboviruses were evaluated using genus-specific Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) assays.
Results: In this study, Culex tarsalis, Culex theileri, and Culex quinquefasciatus were detected, including the first recorded presence of Culex tarsalis in Iran. No infections with alphavirus, flavivirus, or phlebovirus were identified in the collected mosquitoes.
Conclusion: Climatic and weather changes are the basis for the growth and spread of vectors and, consequently, the spread of arboviral diseases, and this issue seems to be very important to the necessity of increasing and continuing entomological and virological studies.
Keywords: Culicidae; Iran; PCR; arboviruses; entomological surveillance; vector.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Jupp P, McIntosh B. Chikungunya virus disease. In: C M Okeoma. (Ed.), The Arboviruses. CRC Press; 2019: 137–57.
-
- Marcondes CB. Generalities and Importance of Arthropod-borne Diseases. Springer; 2017.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
