Impact of hyaluronic acid-modified hafnium metalorganic frameworks containing rhynchophylline on Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 40109770
- PMCID: PMC11920763
- DOI: 10.1515/biol-2022-1043
Impact of hyaluronic acid-modified hafnium metalorganic frameworks containing rhynchophylline on Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
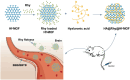
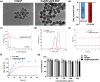
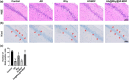
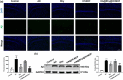
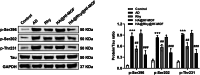
Rhynchophylline (Rhy) is an attractive candidate, harboring ameliorative effects on Alzheimer's disease (AD). Nevertheless, its application is impeded by its low water solubility and poor bioavailability. Here we synthesized and characterized the Rhy-loaded hyaluronic acid-modified hafnium metal-organic frameworks (HA@Rhy@Hf-MOF). The drug release profiles of free Rhy from HA@Rhy@Hf-MOF were evaluated, and the cellular toxicity was assessed through Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay. In vivo experiments included behavioral experiments of various murine capabilities, with neuronal damage appraised through Hematoxylin and Eosin staining and Nissl staining. Subsequently, the formation of AD-related amyloid beta (Aβ) plaques formation and Tau phosphorylation were measured. The HA@Rhy@Hf-MOF with spherical shape were presented as uniformly dispersed and with a negative charge, exhibiting a pronounced pharmacological sustained-release effect and minimal cellular toxicity. Findings from the Morris water maze test, novel object recognition test, and elevated plus maze test substantiated that HA@Rhy@Hf-MOF effectively mitigated cognitive deficiency and anxiety, and enhanced spatial learning in AD mice. Immunofluorescence staining and Western blot both illustrated that HA@Rhy@Hf-MOF could attenuate hippocampal Aβ formation and deposition, as well as tau hyperphosphorylation. In conclusion, HA@Rhy@Hf-MOF exerts its therapeutic efficacy against AD by targeting the deposition of Aβ plaques and inhibiting site-specific phosphorylation of Tau.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Rhynchophylline; amyloid beta; metal-organic frameworks; neurodegenerative disorder; tau protein phosphorylation.
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Demirel G, Sanajou S, Yirun A, Cakir DA, Berkkan A, Baydar T, et al. Evaluation of possible neuroprotective effects of virgin coconut oil on aluminum-induced neurotoxicity in an in vitro Alzheimer’s disease model. J Appl Toxicol. 2023;44:609–22. - PubMed
-
- Ng YP, Or TCT, Ip NY. Plant alkaloids as drug leads for Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem Int. 2015;89:260–70. - PubMed
-
- Xian Y-F, Lin Z-X, Zhao M, Mao Q-Q, Ip S-P, Che C-T. Uncaria rhynchophylla ameliorates cognitive deficits induced by D-galactose in mice. Planta Med. 2011;77:1977–83. - PubMed
-
- Fujiwara H, Iwasaki K, Furukawa K, Seki T, He M, Maruyama M, et al. Uncaria rhynchophylla, a Chinese medicinal herb, has potent antiaggregation effects on Alzheimer’s β‐amyloid proteins. J Neurosci Res. 2006;84:427–33. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
