Gli pathway-targeted Co(iii) Schiff base complexes inhibit migration of basal cell carcinoma cells
- PMID: 40109920
- PMCID: PMC11920859
- DOI: 10.1039/d5ra00326a
Gli pathway-targeted Co(iii) Schiff base complexes inhibit migration of basal cell carcinoma cells
Abstract
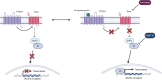
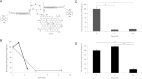
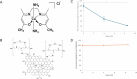
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC) is the most frequently diagnosed cancer globally and affects about one in five Americans. Given the frequency of diagnosis, it is surprising that there are very few therapeutic options. Surgical removal is currently the most common treatment option; however, this can lead to noticeable scarring and cosmetic issues. As a result, there is a compelling interest in developing non-invasive therapeutic approaches to this disease. Here, we introduce a new transition metal-DNA derivative called CoGli-GOPEI that inhibits the migration of murine ASZ BCC cells in laboratory experiments. Notably, this complex significantly outperforms two established hedgehog-pathway inhibitors: GANT-61 (an investigational compound) and vismodegib (an FDA-approved drug). These inhibitors target the hedgehog signaling pathway-specifically the Gli family of transcription factors-to slow cancer progression. By effectively reducing cell migration, CoGli-GOPEI offers a less invasive alternative to traditional treatments like surgical resection and chemotherapy. Our results highlight how targeting the Gli transcription factors within the hedgehog pathway can create a novel therapeutic strategy against BCC. The ultimate goal of these new derivates is to reduce the spread of cancer cells while minimizing the downsides of surgery.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures

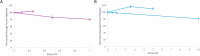
Similar articles
-
Delivery of Targeted Co(III)-DNA Inhibitors of Gli Proteins to Disrupt Hedgehog Signaling.Bioconjug Chem. 2022 Apr 20;33(4):643-653. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.2c00063. Epub 2022 Mar 10. Bioconjug Chem. 2022. PMID: 35271256 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive review of the role of the hedgehog pathway and vismodegib in the management of basal cell carcinoma.Curr Med Res Opin. 2015 Apr;31(4):743-56. doi: 10.1185/03007995.2015.1018988. Epub 2015 Mar 17. Curr Med Res Opin. 2015. PMID: 25690490 Review.
-
Genomic testing, tumor microenvironment and targeted therapy of Hedgehog-related human cancers.Clin Sci (Lond). 2019 Apr 29;133(8):953-970. doi: 10.1042/CS20180845. Print 2019 Apr 30. Clin Sci (Lond). 2019. PMID: 31036756 Review.
-
Synergistic cross-talk of hedgehog and interleukin-6 signaling drives growth of basal cell carcinoma.Int J Cancer. 2018 Dec 1;143(11):2943-2954. doi: 10.1002/ijc.31724. Epub 2018 Oct 1. Int J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29987839 Free PMC article.
-
Hedgehog signaling pathway and its targets for treatment in basal cell carcinoma.J Exp Pharmacol. 2012 Dec 14;4:173-85. doi: 10.2147/JEP.S28553. eCollection 2012. J Exp Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 27186130 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

