Changes in the gut microbiome due to diarrhea in neonatal Korean indigenous calves
- PMID: 40109976
- PMCID: PMC11921620
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1511430
Changes in the gut microbiome due to diarrhea in neonatal Korean indigenous calves
Abstract
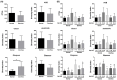
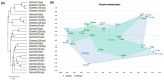
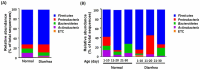
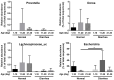
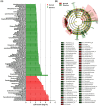
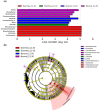
Studies on gut microbiome changes in neonatal Korean indigenous calves with diarrhea are rare. In this study, 14 normal calves and 11 calves with diarrhea were selected from Korean indigenous calves up to 30 days of age and classified into three groups at 10-day intervals (1-10, 11-20, and 21-30 days). Feces from 25 calves were collected, and the diversity, similarity, structure, and correlation of the gut microbiome were analyzed. Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, and Proteobacteria were predominant in the taxonomic composition of the gut microbiome of the calves regardless of the presence of diarrhea. However, Proteobacteria increased and Bacteroidetes and Actinobacteria decreased in calves with diarrhea. In addition, calves with diarrhea showed a significant decrease in the diversity of the gut microbiome, especially for anaerobic microorganisms Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, Gemmiger formicilis, and Collinsella aerofaciens. The microbial communities in calves with diarrhea and normal calves were distinct. By analyzing the microorganisms that showed correlation with diarrhea and age using linear discriminant analysis effect size, at the genus level, Prevotella and Lachnospiraceae_uc were significantly related in the normal (11-20 days) group whereas Enterobacterales, Gammaproteobacteria, Enterobacteriaceae, Escherichia, and Proteobacteria were significantly associated with diarrhea in the 11-20 days group. Futhermore, the normal (21-30 days) group showed significant correlation with Blautia, Provotellaceae, Muribaculaceae, Christensenellaceae, and Catenella, whereas the diarrhea (21-30 days) group showed significant correlation with Dorea. The microorganisms associated with diarrhea in calves were mainly known as harmful microorganisms, we confirmed that there is a relationship between the increase in harmful bacteria and diarrhea. These results show that diarrhea significantly affects the gut microbiome of Korean indigenous calves. The changes in the gut microbiome of Korean indigenous calves observed in this study could be helpful in predicting and managing diarrhea calves, and furthermore, in establishing preventive measures for calf diarrhea through management of gut microbiome.
Keywords: diarrhea; diversity; gut microbiome; linear discriminant analysis effect size; neonatal Korean indigenous calves; taxonomic composition.
Copyright © 2025 Ku, Lee, Jung, Choi and Park.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dynamic Changes in Fecal Microbial Communities of Neonatal Dairy Calves by Aging and Diarrhea.Animals (Basel). 2021 Apr 13;11(4):1113. doi: 10.3390/ani11041113. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33924525 Free PMC article.
-
Rotavirus-mediated alteration of gut microbiota and its correlation with physiological characteristics in neonatal calves.J Microbiol. 2019 Feb;57(2):113-121. doi: 10.1007/s12275-019-8549-1. Epub 2018 Nov 19. J Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30456757 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal Changes in Fecal Unabsorbed Carbohydrates Relative to Perturbations in Gut Microbiome of Neonatal Calves: Emerging of Diarrhea Induced by Extended-Spectrum β-lactamase-Producing Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli.Front Microbiol. 2022 Jul 7;13:883090. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.883090. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35875583 Free PMC article.
-
Gallstone Disease, Obesity and the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio as a Possible Biomarker of Gut Dysbiosis.J Pers Med. 2020 Dec 25;11(1):13. doi: 10.3390/jpm11010013. J Pers Med. 2020. PMID: 33375615 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut Microbiota and Its Repercussion in Parkinson's Disease: A Systematic Review in Occidental Patients.Neurol Int. 2023 Jun 13;15(2):750-763. doi: 10.3390/neurolint15020047. Neurol Int. 2023. PMID: 37368331 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bendali F., Sanaa M., Bichet H., Schelcher F. (1999). Risk factors associated with diarrhoea in newborn calves. Vet. Res. 30, 509–522., PMID: - PubMed
-
- Brunkwall L., Ericson U., Nilsson P. M., Orho-Melander M., Ohlsson B. (2021). Self-reported bowel symptoms are associated with differences in overall gut microbiota composition and enrichment of Blautia in a population-based cohort. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 36, 174–180. doi: 10.1111/jgh.15104, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Carroll I. M., Ringel-Kulka T., Siddle J. P., Ringel Y. (2012). Alterations in composition and diversity of the intestinal microbiota in patients with diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 24, 521–e248. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.2012.01891.x, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

