Ergosterone ameliorates RRR-induced spleen deficiency by gut microbiota-gut metabolites and P38MAPK signaling pathway
- PMID: 40109979
- PMCID: PMC11920137
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1501068
Ergosterone ameliorates RRR-induced spleen deficiency by gut microbiota-gut metabolites and P38MAPK signaling pathway
Abstract
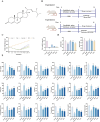
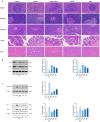
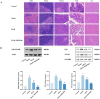
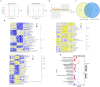
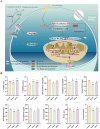
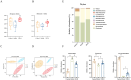
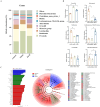
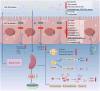
Spleen deficiency is an important immune and digestive system change. Ergosterone (ER) is bioactive steroid; however, to date, no relevant studies have explored its potential efficacy in treating spleen deficiency. The aim of the present study was to investigate the therapeutic effects and mechanism of action of ER on spleen deficiency syndrome induced by Rhei Radix et Rhizoma (RRR). RRR was used to induce the development of a spleen deficiency rat model to observe changes in body weight and pathological changes in organ tissues. Additionally, the levels of relevant immune factors and gastrointestinal hormones were measured, as well as the expression of intestinal tight junction proteins and the P38MAPK signaling pathway. Changes in intestinal microbiota and metabolites were measured, and the effect of ER on the RRR-induced spleen deficiency rat model was evaluated. ER notably alleviated the symptoms of RRR-induced spleen deficiency induced in rats and offered protection against organ damage. Ergosterone can increase the expression of immunoglobulins, inhibits the increase in inflammatory factors, improve gastrointestinal hormone disorders, protect the intestinal mucosa, and repair intestinal barrier damage. The ER-treated group exhibited substantial upregulation of claudin and occludin mRNA and protein expression levels in the colonic tissue. Additionally, ER inhibited the P38MAPKsignaling pathway, thereby improving RRR induced spleen deficiency syndrome in rats. ER also influences the metabolic pathways of protein digestion and absorption, biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids, and arachidonic acid metabolism. In addition, ER can regulate and enhance the composition of intestinal flora in rats with spleen deficiency, increase the diversity of dominant flora, and inhibit the proliferation of harmful bacteria. ER can treat spleen deficiency syndrome by enhancing immune function, improving gastrointestinal function, repairing the intestinal barrier, and regulating intestinal flora and intestinal metabolites.
Keywords: P38MAPK; gut metabolomic; gut microbiota; intestinal barrier; spleen deficiency.
Copyright © 2025 Liu and Bao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Kidney-tonifying blood-activating decoction delays ventricular remodeling in rats with chronic heart failure by regulating gut microbiota and metabolites and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase/p65 nuclear factor kappa-B/aquaporin-4 signaling pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Aug 10;330:118110. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118110. Epub 2024 Apr 3. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38580189
-
Shenling Baizhu Decoction treats ulcerative colitis of spleen-deficiency and dampness obstruction types by targeting 'gut microbiota and galactose metabolism-bone marrow' axis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Dec 5;335:118599. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118599. Epub 2024 Jul 21. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39043352
-
Differential effect of polysaccharide and nonpolysaccharide components in Sijunzi decoction on spleen deficiency syndrome and their mechanisms.Phytomedicine. 2021 Dec;93:153790. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153790. Epub 2021 Oct 8. Phytomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34710756
-
FMT and TCM to treat diarrhoeal irritable bowel syndrome with induced spleen deficiency syndrome- microbiomic and metabolomic insights.BMC Microbiol. 2024 Oct 26;24(1):433. doi: 10.1186/s12866-024-03592-y. BMC Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39455910 Free PMC article.
-
Deep-Fried Atractylodis Rhizoma Protects against Spleen Deficiency-Induced Diarrhea through Regulating Intestinal Inflammatory Response and Gut Microbiota.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 23;21(1):124. doi: 10.3390/ijms21010124. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31878055 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen R., Yang M., Peng C., Yin D. K., Zhang Y. J., Xu F., et al. . (2023). Pharmacodynamics research on danggui-shaoyao-san through body fluid indexes of spleen deficiency-water dampness rats using bioimpedance technology. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 25, 1602–1616. 10.2174/0113892010243018231025065109 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen H., Chen D. Q., Li Q. F., Li P. F., Chen H., Zhao Y. Y. (2014). Research progress on pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and determination of ergosta-4,6,8(14),22-tetraen-3-one. China J. Chin. Mater. Medi. 39, 3905–3909. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

