Clinical Impact of CD19 Expression Assessed by Quantitative PCR in Lymphoma Patients Undergoing CAR-T Therapy
- PMID: 40110072
- PMCID: PMC11920814
- DOI: 10.1002/jha2.70015
Clinical Impact of CD19 Expression Assessed by Quantitative PCR in Lymphoma Patients Undergoing CAR-T Therapy
Abstract
Introduction: Current guidelines do not mandate CD19 tumor expression assessment before chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapy in large B-cell lymphoma (LBCL) patients due to limitations of immunohistochemistry (IHC) or flow cytometry. Quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) offers a more sensitive alternative for detecting CD19 expression, with the primary advantage that mRNA can be easily extracted from paraffin-embedded tissues.
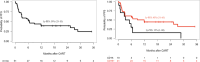
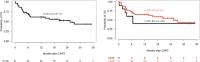
Methods & results: In our study, we included 51 adult patients with LBCL treated with axicabtagene ciloleucel. Among them, 16 were classified as CD19-negative by IHC; however, qPCR reclassified six (37.5%) as CD19-positive. We then compared the outcomes between consistently CD19-negative (IHC-qPCR-) and CD19-positive (IHC+ and IHC-qPCR+) patients. CD19-negative cohort showed worse 1-year progression-free survival (15 vs. 45%, p = 0.044) and a trend toward shorter duration of response (29 vs. 55%, p = 0.065). Only one (10%) of the CD19-negative patients remained alive and disease-free at last follow-up (6 months), having previously responded to bridge therapy.
Discussion: If confirmed in a large patient cohort, these findings could form the basis for modifying current patient selection criteria. Consistently negative patients may be suboptimal candidates for anti-CD19 CAR-T therapy. Alternative therapeutic options, such as bispecific antibodies or polatuzumab-based regimens, could be considered for this subset of patients.
Keywords: CAR‐T therapy; CD19 tumor expression; large B‐cell lymphoma; quantitative PCR.
© 2025 The Author(s). eJHaem published by British Society for Haematology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Jacobson C. A. , Munoz J. , Sun F., et al., “Real‐World Outcomes With Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapies in Large B Cell Lymphoma: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis,” Transplant Cell Ther 30 (2024): 77.e1–77.e15. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
