Integrated single-cell analysis reveals the regulatory network of disulfidptosis-related lncRNAs in bladder cancer: constructing a prognostic model and predicting treatment response
- PMID: 40110199
- PMCID: PMC11919679
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1527036
Integrated single-cell analysis reveals the regulatory network of disulfidptosis-related lncRNAs in bladder cancer: constructing a prognostic model and predicting treatment response
Abstract
Background: Disulfidptosis is a newly discovered form of cell death, and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) play a crucial role in tumor cell growth, migration, recurrence, and drug resistance, particularly in bladder cancer (BLCA). This study aims to investigate disulfidptosis-related lncRNAs (DRLs) as potential prognostic markers for BLCA patients.
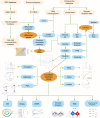
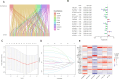
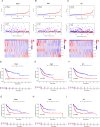
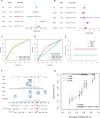
Methods: Utilizing single-cell sequencing data, RNA sequencing data, and corresponding clinical information sourced from the GEO and TCGA databases, this study conducted cell annotation and intercellular communication analyses to identify differentially expressed disulfide death-related genes (DRGs). Subsequently, Pearson correlation and Cox regression analyses were employed to discern DRLs that correlate with overall survival. A prognostic model was constructed through LASSO regression analysis based on DRLs, complemented by multivariate Cox regression analysis. The performance of this model was rigorously evaluated using Kaplan-Meier analysis, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves, and area under the ROC curve (AUC). Furthermore, this investigation delved into the potential signaling pathways, immune status, tumor mutation burden (TMB), and responses to anticancer therapies associated with varying prognoses in patients with BLCA.
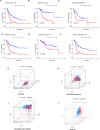
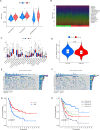
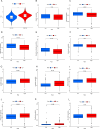
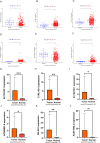
Results: We identified twelve differentially expressed DRGs and elucidated their corresponding intercellular communication relationships. Notably, epithelial cells function as ligands, signaling to other cell types, with the interactions between epithelial cells and both monocytes and endothelial cells exhibiting the strongest connectivity. This study identified six DRLs in BLCA-namely, C1RL-AS1, GK-AS1, AC134349.1, AC104785.1, AC011092.3, and AC009951.6, and constructed a nomogram to improve the predictive accuracy of the model. The DRL features demonstrated significant associations with various clinical variables, diverse immune landscapes, and drug sensitivity profiles in BLCA patients. Furthermore, RT-qPCR validation confirmed the aberrant expression levels of these DRLs in BLCA tissues, affirming the potential of DRL characteristics as prognostic biomarkers.
Conclusion: We established a DRLs model that serves as a predictive tool for the prognosis of BLCA patients, as well as for assessing tumor mutation burden, immune cell infiltration, and responses to immunotherapy and targeted therapies. Collectively, this study contributes valuable insights toward advancing precision medicine within the context of BLCA.
Keywords: bladder cancer; disulfidptosis; immune microenvironment; lncRNA; prognostic model; sequencing; single-cell RNA.
Copyright © 2025 Xiao, Liu, Gong, Lai, Luo, He, Zou and He.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

