Evaluating the role of PCSK9 inhibitors in reducing cardiovascular events among statin-intolerant patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40110272
- PMCID: PMC11918597
- DOI: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000002927
Evaluating the role of PCSK9 inhibitors in reducing cardiovascular events among statin-intolerant patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: To assess the efficacy and safety of Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 (PCSK9) inhibitors in reducing major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in statin-intolerant patients, focusing on low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) reduction and cardiovascular outcomes.
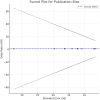
Methods: A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted according to the PRISMA guidelines. Randomised control trails (RCTs) and observational studies from PubMed, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science databases were included. Independent reviewers extracted the data, and the analyses were performed using fixed- and random-effects models. Heterogeneity was evaluated using the I2 statistic and publication bias was assessed using Egger's test.
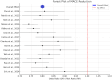
Results: Fifteen studies involving 69-18 924 participants were included. PCSK9 inhibitors reduced LDL-C levels by 50-70% and lowered the risk of MACE by 12% (OR 0.88). Minimal heterogeneity (I2 = 0%) indicated consistency across studies. Subgroup analysis showed greater efficacy in high-risk populations (e.g., acute coronary syndrome and familial hypercholesterolemia). Adverse events were mild, with minimal muscle-related side effects.
Conclusion: PCSK9 inhibitors are effective and safe alternatives for LDL-C reduction and cardiovascular risk mitigation in patients with statin intolerance. Their efficacy, favorable safety profile, and consistency across studies highlight their potential for managing dyslipidemia, particularly in high-risk groups. Further research on long-term outcomes is required.
Keywords: LDL-C reduction; PCSK9 inhibitors; cardiovascular risk; lipid-lowering therapy; major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE); statin intolerance.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare to have no conflicts of interest relevant to this study.
Figures
References
-
- Bernocchi O, Casula M, Scotti L, et al. . LDL-cholesterol reduction with PCSK9 inhibitors: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2017;27:e8.
-
- Boccara F, Kumar PN, Caramelli B, et al. . Evolocumab in HIV-infected patients with dyslipidemia: primary results of the randomized, double-blind BEIJERINCK study. J Am Coll Cardiol 2020;75:2570–84. - PubMed
-
- Davidson E, Snider M, Bartsch K, et al. . Evaluation of the use of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) inhibitors in statin intolerant patients of an outpatient lipid clinic. J Clin Lipidol 2017;11:822–23.
-
- Gupta K, Balachandran I, Foy J, et al. . Highlights of cardiovascular disease prevention studies presented at the 2023 American College of Cardiology Conference. Curr Atheroscler Rep 2023;25:309–21. - PubMed
-
- Hoogeveen R, Opstal TS, Kaiser Y, et al. . Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 antibodies attenuate arterial wall inflammation in statin intolerant patients in absence of crp change. Atherosclerosis 2019;287:e12.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous