Development of Repetitive Mechanical Oscillation Needle-Free Injection through Electrically Induced Microbubbles
- PMID: 40110347
- PMCID: PMC11919823
- DOI: 10.34133/cbsystems.0225
Development of Repetitive Mechanical Oscillation Needle-Free Injection through Electrically Induced Microbubbles
Abstract
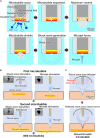
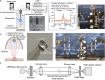
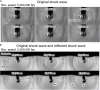
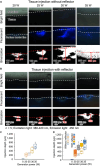
We previously developed a novel needle-free reagent injection method based on electrically induced microbubbles. The system generates microbubbles and applies repetitive mechanical oscillation associated with microbubble dynamics to perforate tissue and introduce a reagent. In this paper, we propose improving the reagent injection depth by reflecting the shock wave through microbubble dynamics. Our results show that the developed shock wave reflection method improves the ability of the electrically induced microbubble injection system to introduce a reagent. The method extends the application potential of electrically induced microbubble needle-free injection.
Copyright © 2025 Yibo Ma et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of Cavitation from Extracorporeal Shock Wave Combined with Sulfur Hexafluoride Microbubble on Myocardial Ultrastructure in Rats.Anatol J Cardiol. 2023 Sep 1;27(9):519-528. doi: 10.14744/AnatolJCardiol.2023.2946. Epub 2023 Jun 7. Anatol J Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 37288863 Free PMC article.
-
Internalization of targeted microbubbles by endothelial cells and drug delivery by pores and tunnels.J Control Release. 2022 Jul;347:460-475. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.05.008. Epub 2022 May 19. J Control Release. 2022. PMID: 35545132
-
Ultrasound-driven microbubble oscillation and translation within small phantom vessels.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2007 Dec;33(12):1978-87. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2007.06.007. Epub 2007 Sep 27. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 17900793
-
The Role of Ultrasound-Driven Microbubble Dynamics in Drug Delivery: From Microbubble Fundamentals to Clinical Translation.Langmuir. 2019 Aug 6;35(31):10173-10191. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b03779. Epub 2019 Feb 4. Langmuir. 2019. PMID: 30653325 Review.
-
Italian Society of Cardiovascular Echography (SIEC) Consensus Conference on the state of the art of contrast echocardiography.Ital Heart J. 2004 Apr;5(4):309-34. Ital Heart J. 2004. PMID: 15185894 Review.
References
-
- Vadlapatla R, Gayakwad S, Yellepeddi V, Wong EY. Needle-free injectors. In: Drug delivery devices and therapeutic systems. Cambridge (MA): Academic Press; 2021. p. 199–211.
-
- Han HS, Hong JY, Kwon TR, Lee SE, Yoo KH, Choi SY, Kim BJ. Mechanism and clinical applications of needle-free injectors in dermatology: Literature review. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20(12):3793–3801. - PubMed
-
- Pingle P, Joshi I, Sodhi RK, Madan J, Mehra NK, Singh PK, Srivastava S, Khatri DK, Singh SB. Needle-free technology for biomedical applications. Multifunct Nano. 2022;149–173.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

