Erythrocyte-derived extracellular vesicles induce endothelial dysfunction through arginase-1 and oxidative stress in type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 40111409
- PMCID: PMC12077887
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI180900
Erythrocyte-derived extracellular vesicles induce endothelial dysfunction through arginase-1 and oxidative stress in type 2 diabetes
Abstract
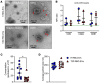
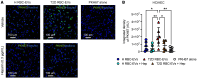
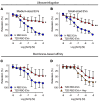
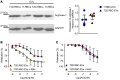
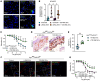
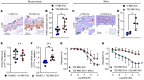
Red blood cells (RBCs) induce endothelial dysfunction in type 2 diabetes (T2D), but the mechanism by which RBCs communicate with the endothelium is unknown. This study tested the hypothesis that extracellular vesicles (EVs) secreted by RBCs act as mediators of endothelial dysfunction in T2D. Despite a lower production of EVs derived from RBCs of T2D patients (T2D RBC-EVs), their uptake by endothelial cells was greater than that of EVs derived from RBCs of healthy individuals (H RBC-EVs). T2D RBC-EVs impaired endothelium-dependent relaxation, and this effect was attenuated following inhibition of arginase in EVs. Inhibition of vascular arginase or oxidative stress also attenuated endothelial dysfunction induced by T2D RBC-EVs. Arginase-1 was detected in RBC-derived EVs, and arginase-1 and oxidative stress were increased in endothelial cells following coincubation with T2D RBC-EVs. T2D RBC-EVs also increased arginase-1 protein in endothelial cells following mRNA silencing and in the endothelium of aortas from endothelial cell arginase-1-knockout mice. It is concluded that T2D-RBCs induce endothelial dysfunction through increased uptake of EVs that transfer arginase-1 from RBCs to the endothelium to induce oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction. These results shed important light on the mechanism underlying endothelial dysfunction mediated by RBCs in T2D.
Keywords: Cardiology; Cardiovascular disease; Diabetes; Endothelial cells; Vascular biology.
Figures

Comment in
- Endothelial dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes: the truth is in the blood
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

