Revolutionizing bone healing: the role of 3D models
- PMID: 40113735
- PMCID: PMC11926310
- DOI: 10.1186/s13619-025-00225-1
Revolutionizing bone healing: the role of 3D models
Abstract
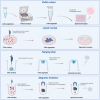
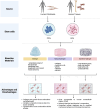
The increasing incidence of bone diseases has driven research towards Bone Tissue Engineering (BTE), an innovative discipline that uses biomaterials to develop three-dimensional (3D) scaffolds capable of mimicking the natural environment of bone tissue. Traditional approaches relying on two-dimensional (2D) models have exhibited significant limitations in simulating cellular interactions and the complexity of the bone microenvironment. In response to these challenges, 3D models such as organoids and cellular spheroids have emerged as effective tools for studying bone regeneration. Adult mesenchymal stem cells have proven crucial in this context, as they can differentiate into osteoblasts and contribute to bone tissue repair. Furthermore, the integration of composite biomaterials has shown substantial potential in enhancing bone healing. Advanced technologies like microfluidics offer additional opportunities to create controlled environments for cell culture, facilitating more detailed studies on bone regeneration. These advancements represent a fundamental step forward in the treatment of bone pathologies and the promotion of skeletal health. In this review, we report on the evolution of in vitro culture models applied to the study of bone healing/regrowth, starting from 2 to 3D cultures and microfluids. The different methodologies of in vitro model generation, cells and biomaterials are presented and discussed.
Keywords: 3D in vitro model; Biomaterial; Bone regeneration; Cell-ECM interaction; Microfluidic; Stem cell.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
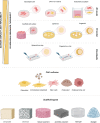
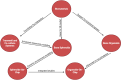
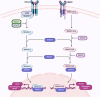
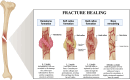
Figures
References
-
- Abbasi, Fatemeh, Mohammad Hossein Ghanian, Hossein Baharvand, Bahman Vahidi, e Mohamadreza Baghaban Eslaminejad. 2018. «Engineering Mesenchymal Stem Cell Spheroids by Incorporation of Mechanoregulator Microparticles». Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials 84 (agosto):74–87. 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2018.04.026. - PubMed
-
- Abu-El-Rub E, Khaswaneh RR, Almahasneh FA, Almazari R, e Ayman Alzu’bi. Adipose Tissue and Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Are Not Really the Same: Investigating the Differences in Their Immunomodulatory, Migratory, and Adhesive Profile. Biochemical Genetics, Marzo. 2024. 10.1007/s10528-024-10724-6. - PubMed
-
- Akiva A, Melke J, Ansari S, Liv N, Van Der Meijden R, Van Erp M, Zhao F, et al. An Organoid for Woven Bone. Adv Func Mater. 2021;31(17):2010524. 10.1002/adfm.202010524.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
