Induction of LY6E regulates interleukin-1β production, potentially contributing to the immunopathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 40114200
- PMCID: PMC11924716
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-025-02140-z
Induction of LY6E regulates interleukin-1β production, potentially contributing to the immunopathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
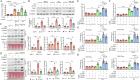
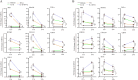
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disorder characterized by the deposition of immune complexes (ICs) in various organs, especially the kidney, leading to lupus nephritis, one of the major and therapeutically challenging manifestations of SLE. Among the various cytokines induced in SLE, type I interferons (IFN-Is) play crucial roles in mediating immunopathogenesis, and anti-IFN-I treatment has been approved for SLE treatment. The uptake of ICs by macrophages results in macrophage activation, which initiates, triggers, and exaggerates immune responses in SLE. After observing the induction of an IFN-stimulated gene, LY6E, in monocytes from SLE patients, we demonstrated the colocalization of both LY6E and a macrophage marker in kidneys from pristane-induced lupus-prone mice and from patients with lupus nephritis. By studying mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages, we showed that LY6E regulated IFN-α- and IC-induced production and secretion of mature interleukin-1β (mIL-1β), foam cell formation and several mitochondria-associated mechanisms, such as the release of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) but not mitochondrial RNA (mtRNA) into the cytosol, the generation of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (mtROS) and ROS, the activation of caspase 1, NLRP3, and the stimulator of interferon genes (STING) signaling pathway, and the activation of cytidine/uridine monophosphate kinase 2 (CMPK2), which were involved in LY6E-mediated immunomodulatory effects. In addition, synergistic effects of a combination of IL-1β and IFN-α and of IL-1β and ICs on the induction of the expression of IFN-stimulated genes were observed. In addition to revealing the proinflammatory roles and mechanisms of LY6E in macrophages, given that various subgroups of macrophages have been identified in the kidneys of patients with lupus nephritis, targeted treatment aimed at LY6E may be a potential therapeutic for lupus nephritis.
Keywords: Interferon-alpha; Interleukin-1; LY6E; Lupus nephritis; Macrophages; Systemic lupus erythematosus.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The use of human blood samples was approved by the IRB (no. 201509825A3) of Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Linko, Taiwan. This study was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures









References
-
- Tsokos GC. The immunology of systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Immunol. 2024;25:1332–43. - PubMed
-
- Rahman A, Isenberg DA. Systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:929–39. - PubMed
-
- Chen PM, Tsokos GC. Mitochondria in the Pathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2022;24:88–95. - PubMed
-
- Caielli S, Wan Z, Pascual V. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Pathogenesis: Interferon and Beyond. Annu Rev Immunol. 2023;41:533–60. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

