[FCN3 Can Serve as A Potential Biomarker for Prognosis and Immunotherapy of Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma]
- PMID: 40114488
- PMCID: PMC11931238
- DOI: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2025.105.01
[FCN3 Can Serve as A Potential Biomarker for Prognosis and Immunotherapy of Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma]
Abstract
Background: Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC) is an important pathological subtype of NSCLC. The complex immune escape mechanism limits the effectiveness of immunotherapy. Ficolin-3 (FCN3) is a crucial immunomodulatory molecule that regulates immune escape by remodeling the tumor microenvironment. However, the role of FCN3 in LUSC remains unclear. This study employed bioinformatics methods to analyze LUSC samples from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. The aim of this study was to explore the potential biological functions and prognostic significance of FCN3 in LUSC.
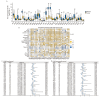
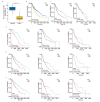
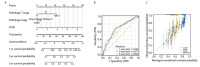
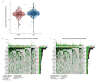
Methods: A pan-cancer analysis characterized the expression patterns and prognostic value of FCN3 across various cancer types. Simultaneously, the expression patterns of FCN3 in LUSC samples from the TCGA database and its relationship with prognosis were analyzed. The Nomogram model and somatic mutation analysis, differential expression analysis, correlation analysis, as well as Gene Ontology (GO), Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG), and Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) were constructed to explore the potential mechanisms of FCN3. Additionally, immune infiltration analysis, immune escape score (TIDE), and correlation analysis of immune-related molecules were used to reveal the regulatory role of high FCN3 levels on immunity in LUSC. Furthermore, the correlation between FCN3 expression characteristics and drug sensitivity was evaluated. Finally, in vitro experiments verified the expression characteristics of FCN3 in LUSC.
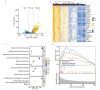
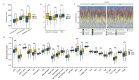
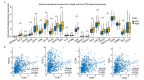
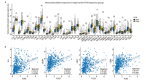
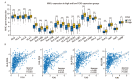
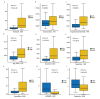
Results: The expression level of FCN3 in LUSC tissues was significantly lower than that in normal tissues. Patients with high FCN3 expression in LUSC had a poorer prognosis compared to those with low expression. Different expression levels of FCN3 were associated with the abundance of immune cell infiltration and immune cell dysfunction. It was also linked to the expression of immune checkpoints, immune stimulatory molecules, major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class molecules, and chemotherapy drug sensitivity.
Conclusions: High expression of FCN3 in LUSC is associated with poor prognosis and is linked to immune cell infiltration, immune-related pathways, and immune-related molecules. FCN3 may be a potential prognostic marker and a new target for immunotherapy in LUSC.
【中文题目:FCN3可作为肺鳞癌预后及免疫治疗 的潜在生物标志物】 【中文摘要:背景与目的 非小细胞肺癌(non-small cell lung cancer, NSCLC)是全球癌症死亡的主要原因。肺鳞状细胞癌(lung squamous cell carcinoma, LUSC)是其重要的病理组织学亚型,免疫逃逸机制复杂,使得免疫治疗的效果有限。Ficolin-3(FCN3)是一种重要的免疫调节分子,它可以通过重塑肿瘤免疫微环境来调节肿瘤的免疫逃逸,但FCN3在LUSC中的作用仍不清楚。本研究使用生物信息学方法对来自癌症基因组图谱(The Cancer Genome Atlas, TCGA)数据库的LUSC样本进行了全面分析,旨在探讨FCN3在LUSC中潜在的生物学功能以及预后意义。方法 泛癌分析表征FCN3的泛癌表达特征及预后价值,同时基于TCGA数据库中的LUSC样本数据,分析FCN3在LUSC中的表达特征及预后关系。通过构建Nomogram模型、体细胞突变分析、差异分析、相关性分析及基因本体(Gene Ontology, GO)、京都基因与基因组百科全书(Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes, KEGG)和基因集富集分析(Gene Set Enrichment Analysis, GSEA)进一步探索FCN3的潜在作用机制。通过免疫浸润分析、免疫逃逸评分、免疫相关分子相关性分析揭示FCN3在LUSC中高表达对免疫的调节作用,同时评估FCN3特征表达与药物敏感性的相关性。体外实验验证FCN3在LUSC中的表达特征。结果 FCN3在LUSC组织中的表达水平显著低于正常组织。高表达FCN3的LUSC患者预后较差。FCN3的不同表达情况与免疫细胞浸润丰度、免疫细胞功能障碍有关联,并且与免疫检查点、免疫刺激分子、主要组织相容性复合体(major histocompatibility complex, MHC)类分子表达及化疗药物敏感性也存在关联。结论 LUSC中FCN3的高表达与不良预后有关,并且FCN3与免疫细胞浸润、相关免疫通路及免疫相关分子有关,FCN3可能是LUSC潜在的预后标志物和免疫治疗新靶点。 】 【中文关键词:FCN3;肺肿瘤;免疫;生物标志物】.
Keywords: Biomarker; FCN3; Immunity; Lung neoplasms.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Unveiling ficolins: diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers linked to the Tumor Microenvironment in Lung Cancer.World J Surg Oncol. 2024 Oct 10;22(1):273. doi: 10.1186/s12957-024-03558-4. World J Surg Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39390580 Free PMC article.
-
Significance of NKX2-1 as a biomarker for clinical prognosis, immune infiltration, and drug therapy in lung squamous cell carcinoma.PeerJ. 2024 May 1;12:e17338. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17338. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38708353 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of RNMT as an immunotherapeutic and prognostic biomarker: From pan-cancer analysis to lung squamous cell carcinoma validation.Immunobiology. 2024 Sep;229(5):152836. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2024.152836. Epub 2024 Jul 16. Immunobiology. 2024. PMID: 39018675
-
Pyroptosis-related long-noncoding RNA signature predicting survival and immunotherapy efficacy in patients with lung squamous cell carcinoma.Clin Exp Med. 2024 Jul 3;24(1):145. doi: 10.1007/s10238-024-01409-w. Clin Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 38960987 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering a cell death-associated signature for predicting prognosis and response to immunotherapy in lung squamous cell carcinoma.Respir Res. 2023 Jul 6;24(1):176. doi: 10.1186/s12931-023-02402-9. Respir Res. 2023. PMID: 37415224 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

