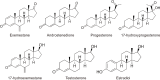
Analytical Interference of Exemestane With Androstenedione Immunoassays
- PMID: 40114653
- PMCID: PMC12187492
- DOI: 10.3343/alm.2024.0362
Analytical Interference of Exemestane With Androstenedione Immunoassays
Abstract
Background: Exemestane, an aromatase inhibitor commonly used for breast cancer treatment, shares structural similarities with sex steroids analyzed in clinical laboratories. We aimed to investigate the influence of exemestane cross-reactivity in the measurement of sex steroids across various immunoassays.
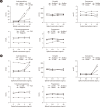
Methods: We conducted a multicenter study involving measurements of androstenedione, testosterone, estradiol, progesterone, and 17-hydroxyprogesterone in serum samples from women undergoing exemestane therapy (N=15; 25 mg/day). Measurements were performed using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) and various commercially available chemiluminescence immunoassays, ELISA, and radioimmunoassay. In-vitro cross-reactivity was assessed by adding exemestane and 17-hydroexemestane to serum samples.
Results: Patients undergoing exemestane therapy had markedly falsely elevated androstenedione results in all immunoassays evaluated (N=4), which correlated with serum exemestane levels. In-vitro experiments confirmed this interference to be caused by cross-reactivity with exemestane. Additionally, one immunoassay yielded falsely elevated estradiol results in 20% of patients. However, in-vitro experiments did not confirm this to be caused by cross-reactivity with exemestane or 17-hydroexemestane.
Conclusions: Exemestane cross-reacts with androstenedione immunoassays, causing falsely elevated results in treated patients. This analytical interference may raise unnecessary concerns, leading to expensive diagnostic workups.
Keywords: Cross-reactivity; Exemestane; Hyperandrogenism; Immunoassay; Immunochemiluminescence; Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures